
SF6 Circuit Breaker Working Principle
SF6 Circuit Breaker Working Principle https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/maxresdefault-5-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gSF6 circuit breakers are one of the most cost-effective solutions for breaking large fault currents. In addition, SF6 gas plays a key role in quenching the arc generated by high currents. As a result, SF6 circuit breakers dominate the high and extra-high voltage switchgear market. Therefore, in this article, we will explain the SF6 circuit breaker working principle step by step.
Table of Contents
- Why We Need a Circuit Breaker
- How SF6 Gas Helps in Quenching the Arc
- SF6 Circuit Breaker Construction
- Step-by-Step Working of SF6 Circuit Breaker
- Key Points of SF6 Circuit Breaker Operation
- Advantages of SF6 Circuit Breakers
- SF6 Circuit Breaker Components
- Summary of SF6 Circuit Breaker Working Principle
- Conclusion
Why We Need a Circuit Breaker
We use a circuit breaker to stop the current flowing through a system. There are two main situations:
- Switching a device on or off.
- Interrupting a fault current.
When a fault occurs, we cannot rely on a regular switch. In such cases, opening the contacts produces an electric arc. Moreover, the intensity of the arc depends on the current. For instance, low-voltage applications produce low-intensity arcs, whereas high-voltage systems generate high-intensity arcs.
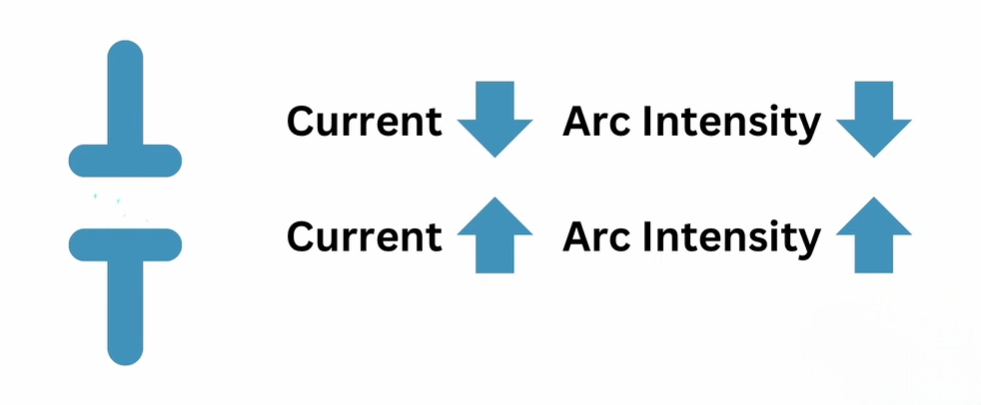
Regular switches cannot handle high fault currents. Therefore, we need a special medium to quench the arc. SF6 gas is one such medium. Another example is a vacuum circuit breaker, which we discussed in a previous article.
How SF6 Gas Helps in Quenching the Arc
The arc occurs because free electrons surround the separating contacts. When voltage acts on the contacts, it ionizes these free electrons. As a result, the voltage across the contacts tries to maintain the current, which therefore keeps the arc alive.
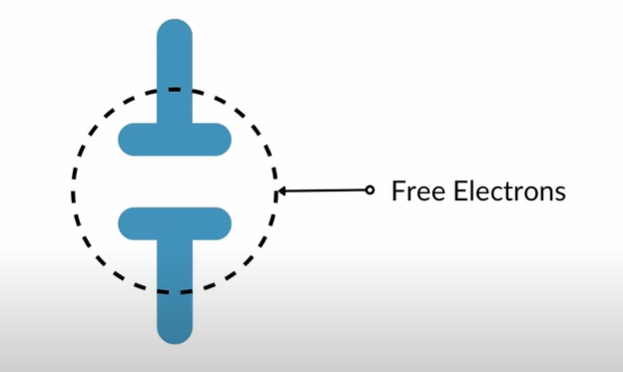
To stop the arc, we must remove or neutralize these free electrons. Vacuum circuit breakers do this by creating a vacuum where there are few electrons. SF6 circuit breakers use the special properties of SF6 gas.
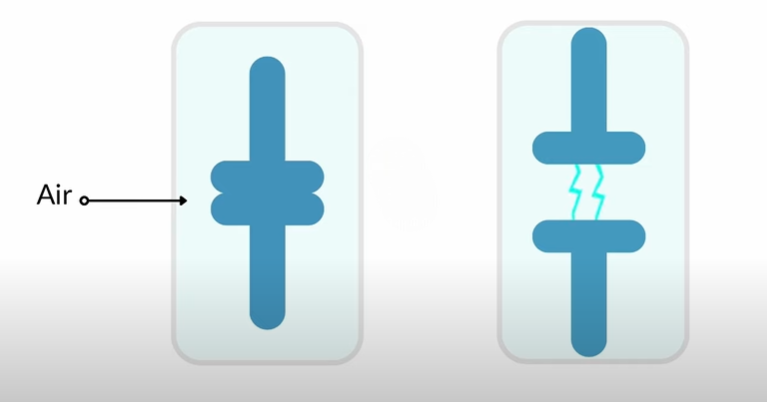
SF6 is an electronegative gas. It attracts free electrons in the air. When SF6 gas surrounds the contacts, it absorbs the electrons. This reduces the arc and helps extinguish it.
SF6 Circuit Breaker Construction
Designers create the contacts of an SF6 circuit breaker differently from those of vacuum circuit breakers. The key components include:
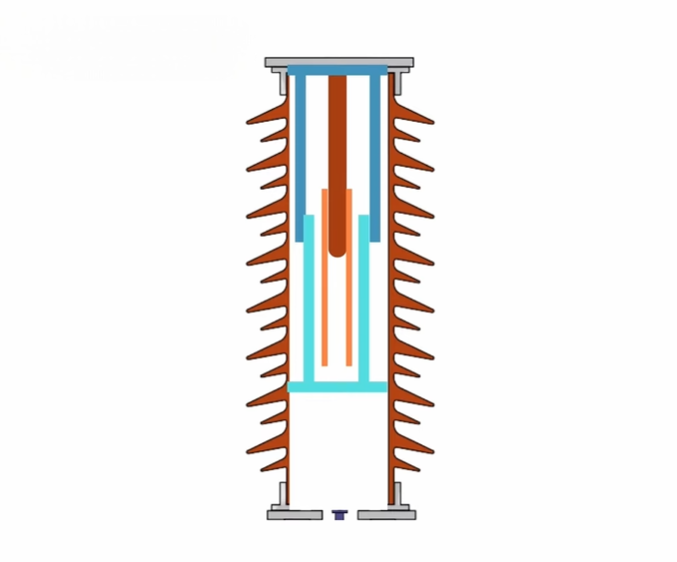
- A porcelain insulator to support the contacts.
- Main contacts carrying normal system current.
- Arcing contacts designed to handle fault currents.
- Pressurized SF6 gas surrounding the contacts.
The main contacts carry the regular current. When a fault occurs, the arcing contacts take over. The arc forms between the arcing contacts. SF6 gas is then concentrated on the arc through nozzles. It absorbs free electrons and extinguishes the arc at the next current zero.
Step-by-Step Working of SF6 Circuit Breaker
Fault Detection and Contact Separation
Relays detect a fault in the system. The circuit breaker receives a trip command from the relay. The main contacts separate first, transferring the current to the arcing contacts.
Arc Formation and SF6 Gas Action
As the arcing contacts separate, an arc forms between them. SF6 gas is blown through nozzles onto the arc. Its electronegative property attracts free electrons, reducing the arc.
The SF6 gas also cools the arc quickly. At the next current zero, the arc is fully extinguished. The system current stops, clearing the fault.
Importance of Dielectric Strength
After the arc is extinguished, the rate of rise of the recovery voltage (RRRV) becomes important. If the RRRV is higher than the dielectric strength, the arc may reignite. This can damage equipment.
Design engineers must ensure that the dielectric strength rises faster than the recovery voltage. This ensures the arc does not reignite and the breaker operates successfully.
Key Points of SF6 Circuit Breaker Operation
- The fault is detected by the relay.
- The main contacts open first.
- Current transfers to the arcing contacts.
- The arcing contacts open, forming an arc.
- The breaker directs pressurized SF6 gas onto the arc.
- SF6 gas absorbs the free electrons and quenches the arc.
- SF6 gas cools the arc.
- The breaker interrupts the current and clears the fault.
Advantages of SF6 Circuit Breakers
SF6 circuit breakers are reliable and efficient. Some of their advantages are:
- High dielectric strength.
- Ability to interrupt large fault currents.
- Excellent cooling properties.
- Long operational life due to less contact erosion.
The main drawback is that SF6 is a strong greenhouse gas. This is leading the industry to explore SF6-free alternatives. Vacuum technology is becoming a potential replacement for high-voltage interruption.
SF6 Circuit Breaker Components
The main components of an SF6 circuit breaker include:
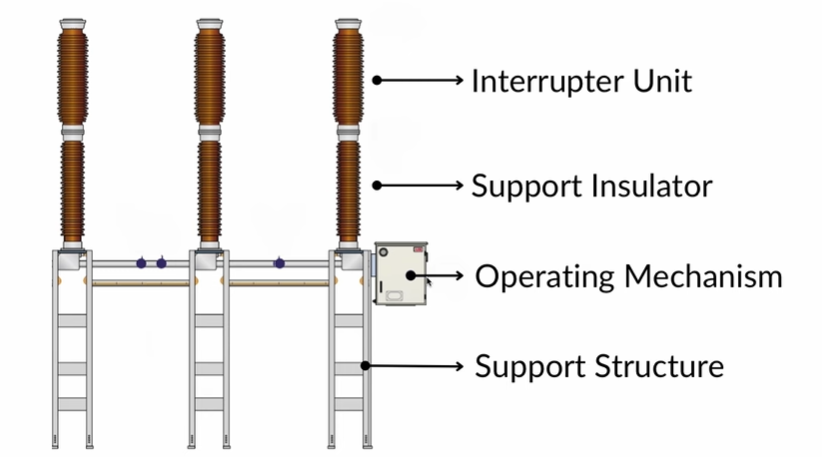
- Interruptor assembly with arcing and main contacts.
- Porcelain insulator for support.
- Operating mechanism connected via an operating rod.
- Support structure for the entire assembly.
The operating mechanism provides the necessary force to open the contacts and separate them properly. Each part ensures the arc is quenched efficiently and safely.
Summary of SF6 Circuit Breaker Working Principle
The SF6 circuit breaker working principle can be summarized as follows:
First, the relay detects the fault. Then, the main contacts open, transferring the current to the arcing contacts. Next, the arcing contacts separate, forming an arc. At this stage, pressurized SF6 gas is blown onto the arc. As a result, the gas absorbs the free electrons, and the arc quenches at the next current zero. Furthermore, the SF6 gas cools the arc, ensuring a safe current interruption.
Overall, this process effectively stops the fault current, thereby protecting the system and all connected equipment.nt.
Conclusion
SF6 circuit breakers are, therefore, a highly effective solution for high-voltage systems. Because of their electronegative properties, they remove free electrons, which quenches arcs efficiently. In addition, SF6 also cools the arc, thereby improving the speed of interruption. Moreover, proper design ensures that the dielectric strength overcomes the recovery voltage, preventing arc reignition and ensuring safe operation.
For a clearer understanding of the SF6 circuit breaker working principle, it is highly recommended to watch the full video by TheElectricalGuy on YouTube. The video explains the process with visuals, which makes it much easier to grasp the construction and operation of SF6 circuit breakers.

- Posted In:
- Switchgear
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 8 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 240K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

