Disadvantages of Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) Substations Explained in Detail
Disadvantages of Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS) Substations Explained in Detail https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/maxresdefault-5-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gGas insulated switchgear has gained strong momentum in recent years across both high-voltage and medium-voltage industries. Many utilities prefer GIS because it offers several advantages over air insulated switchgear. These advantages include compact size, higher reliability, and better performance in limited spaces. However, every technology comes with limitations. Along with its benefits, GIS also has several major drawbacks. Understanding these disadvantages is important before selecting this technology for a substation.

This article explains the disadvantages of Gas Insulated Switchgear/Substation in detail. The discussion follows the same flow as the referenced video and covers all the points mentioned in the transcript. No additional technical information has been added. The aim is to help readers understand where GIS faces challenges and why these limitations matter in real-world applications.
Table of Contents
- High Reliability but Serious Impact During Internal Faults
- Manufacturer Dependency Limits Flexibility
- Environmental Concerns Due to SF6 Gas Usage
- High Initial Cost Compared to AIS
- Indoor Installation Requirements Add Operational Burden
- Maintenance and Repair Challenges
- Choosing GIS Despite Its Disadvantages
- Importance of Understanding the Disadvantages
- Conclusion: Evaluating the Disadvantages of Gas Insulated Switchgear/Substation
High Reliability but Serious Impact During Internal Faults
Gas insulated switchgear is known for its high reliability. Internal faults in GIS are very rare. This reliability is one of the main reasons utilities adopt this technology. However, when an internal fault does occur, it creates a serious problem. The major issue in such cases is the very long outage time required for repair.
To understand this drawback clearly, it is useful to compare GIS with air insulated switchgear. In an AIS system, components such as current transformers are standalone devices. If a current transformer fails, maintenance teams can remove and replace it easily. In most cases, they restore the supply within six or seven hours.
In contrast, gas insulated switchgear uses a fully interconnected design. The system encloses and seals all components together. Because of this structure, technicians cannot remove a single faulty component on its own. If a current transformer fails inside a GIS system, the maintenance team must remove the entire bay for repair or replacement. This requirement increases repair time significantly. As a result, the outage lasts much longer than in AIS. Internal faults occur rarely in GIS, but they create serious operational impact when they do. This extended outage time remains a major disadvantage of Gas Insulated Switchgear/Substation.
Manufacturer Dependency Limits Flexibility
Another important disadvantage of gas insulated switchgear is its dependency on manufacturers. There are many GIS manufacturers in the market, and each follows its own design standards. Dimensions, internal architecture, and interface designs differ from one manufacturer to another. This lack of standardization creates problems during future expansion or modification.

When a GIS substation needs expansion, such as adding two new bays, the process is not straightforward. Equipment from one manufacturer often cannot be directly integrated with equipment from another manufacturer. To make different systems compatible, custom adapter plates may be required. Designing these adapter plates is complex and time-consuming. It also adds extra cost to the project.
In comparison, air insulated switchgear offers much greater flexibility. AIS systems do not depend heavily on manufacturer-specific designs. In air insulated switchgear, engineers can install equipment from different manufacturers in the same substation. They can add or modify bays without facing major design challenges. This flexibility makes expansion simple and cost-effective. In contrast, gas insulated switchgear restricts such changes. Manufacturer dependency reduces flexibility and complicates future upgrades. These limitations form a clear disadvantage of Gas Insulated Switchgear/Substation.
Environmental Concerns Due to SF6 Gas Usage
One of the most critical drawbacks of gas insulated switchgear is the use of SF6 gas. GIS requires SF6 in very large quantities to provide insulation. For example, a single 145 kV GIS bay may require around 130 to 150 kilograms of SF6 gas. This large volume creates serious environmental concerns.
SF6 is one of the most powerful greenhouse gases. Its global warming potential is extremely high. Once released into the environment, it can remain there for nearly 3,000 years. Even small leaks can cause long-term environmental damage. Because of this, SF6 usage has become a major concern for regulators and environmental agencies worldwide.
Due to these risks, there is a growing push toward SF6-free technologies. Some alternatives, such as clean air insulation, are now available. These solutions aim to reduce environmental impact. However, most existing GIS installations still rely on SF6 gas. As a result, environmental impact remains a significant disadvantage of Gas Insulated Switchgear/Substation.
High Initial Cost Compared to AIS
Cost is another major factor that affects the adoption of GIS. Compared to air insulated switchgear, the initial cost of gas insulated switchgear is very high. AIS remains the most economical option available for switchgear installations. GIS requires higher investment in equipment, installation, and handling.
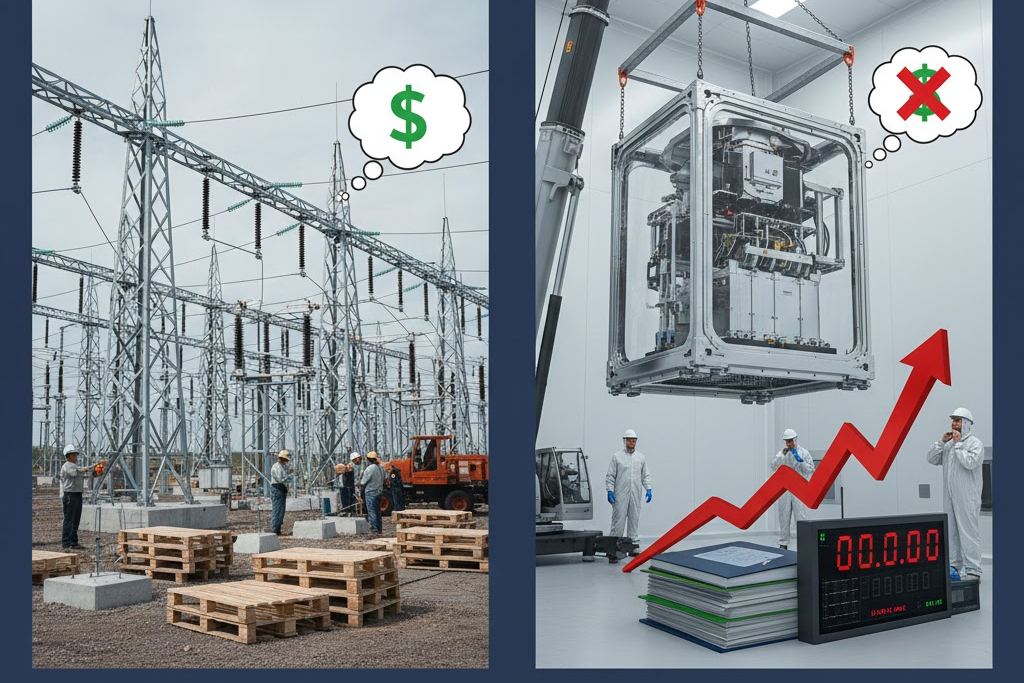

While evaluating cost, it is important to consider the lifecycle cost rather than only the initial investment. In some applications, GIS may prove cost-effective over its entire operating life. Factors such as reduced maintenance and space savings can help balance the higher upfront cost. However, this is not always the case.
In many projects, the high initial cost of GIS becomes a major limitation. Budget constraints may prevent utilities from choosing GIS even when its advantages are attractive. Therefore, the high upfront investment is a significant disadvantage of Gas Insulated Switchgear/Substation.
Indoor Installation Requirements Add Operational Burden
Gas insulated switchgear is mostly installed indoors. Although outdoor GIS options exist, most systems require a dedicated building. This requirement adds another layer of complexity to the project. A proper structure must be built to house the switchgear.
The indoor environment requires careful maintenance to ensure reliable operation. Teams must keep the area clean at all times. They must control dust, moisture, and temperature changes. In many installations, operators install air conditioning systems to maintain stable conditions. These requirements increase operational effort and ongoing maintenance responsibility.
In contrast, engineers usually install air insulated switchgear outdoors. After installation, the equipment operates under natural environmental conditions. AIS does not need special buildings or climate control systems. Maintenance teams handle inspections and repairs more easily, and infrastructure costs stay lower. Because of these differences, indoor installation remains a clear disadvantage of Gas Insulated Switchgear/Substation.
Maintenance and Repair Challenges
Although GIS uses a sealed design and needs maintenance less often, maintenance becomes difficult when issues arise. Technicians face challenges while accessing internal components. Repairs require specialized tools and skilled personnel. Major repair work often leads to extended outages.
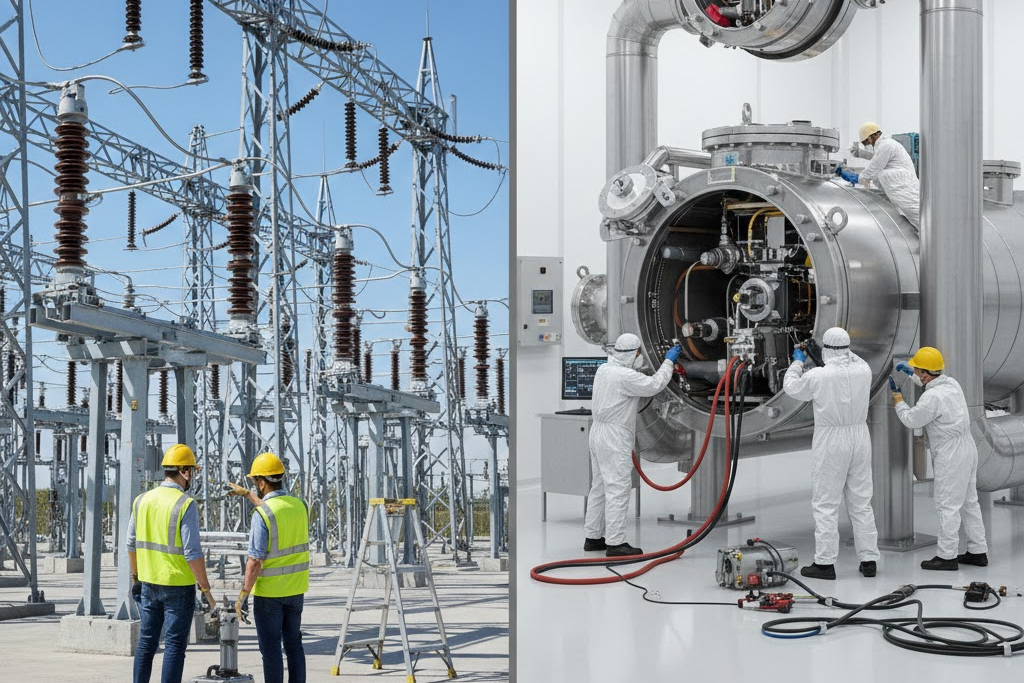

In contrast, AIS offers easy access to components. Fault identification and isolation are simpler. Repairs can be completed faster, which helps restore supply quickly. This difference affects outage planning and system availability. Utilities must consider these maintenance challenges when choosing GIS technology.
Choosing GIS Despite Its Disadvantages
Despite these disadvantages, gas insulated switchgear continues to be widely used. Certain applications require compact designs, especially in urban areas where space is limited. In such cases, AIS may not be feasible at all. GIS becomes the only practical option.
The choice between GIS and AIS depends on multiple factors. Space availability, environmental conditions, cost, and reliability requirements all play important roles. There is no single solution that fits every situation. Understanding the disadvantages helps engineers and planners make informed decisions.
Importance of Understanding the Disadvantages
Often, discussions around GIS focus only on its advantages. The disadvantages receive less attention. This creates unrealistic expectations and can lead to poor planning decisions. A balanced understanding of both benefits and drawbacks is essential.
Knowing the disadvantages of Gas Insulated Switchgear/Substation allows better system design. It helps in planning mitigation strategies and reducing operational risks. Informed decisions lead to more reliable and cost-effective power systems.
Conclusion
Gas insulated switchgear offers several advantages, but it also has clear limitations. Long outage times during internal faults, limited expansion flexibility, environmental concerns related to SF6 gas, high initial costs, and indoor installation requirements are major drawbacks. Each of these factors plays an important role in technology selection.
Understanding these disadvantages is critical before adopting GIS for any project. For a clearer and more visual explanation, it is recommended to watch the referenced video for better understanding.

- Posted In:
- Switchgear
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 8 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 240K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

