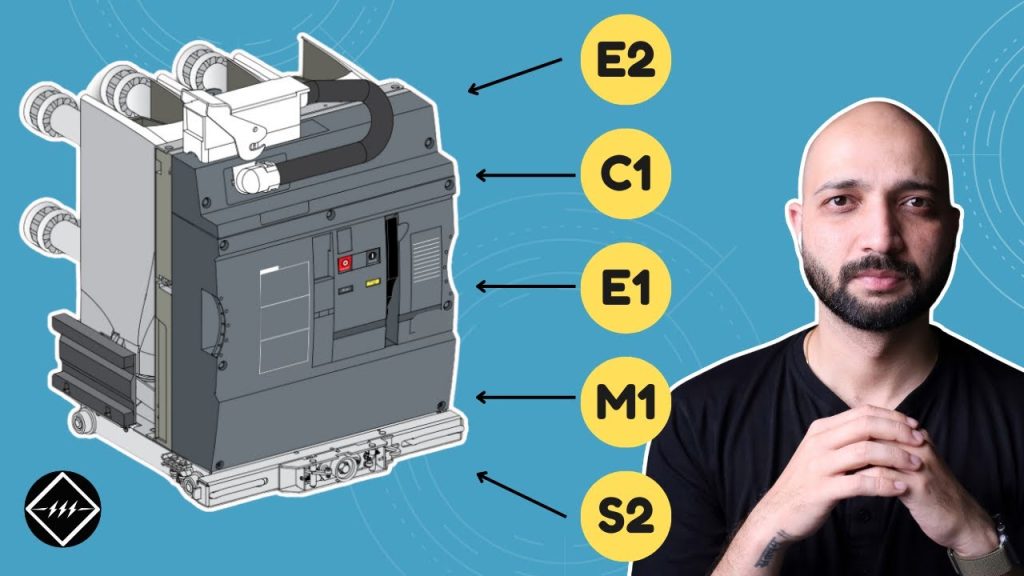
What Is Circuit Breaker Classes and Why They Matter
What Is Circuit Breaker Classes and Why They Matter https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/maxresdefault-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gCircuit breakers are classified into different classes to define their performance and suitability for specific applications. These classes represent how well a circuit breaker can withstand electrical stress, mechanical operations, and system conditions. International standards define many of these classes, and manufacturers list them on the circuit breaker nameplate.
To clearly understand what is circuit breaker classes, it is important to know why these classes exist. A circuit breaker does not face the same conditions in every system. Some applications demand higher endurance, while others require better switching performance. Because of this, standards define classes to indicate how suitable a breaker is for a particular application.
A simple example is IP ratings in mobile phones. A phone with an IP67 rating performs better under harsh conditions than one with an IP55 rating because it has passed stricter tests.

Circuit breaker classes show how extensively standards have tested a breaker and where engineers should use it. These classes help engineers choose the correct breaker and avoid system failures.
Table of Contents
- Electrical Endurance Class in Circuit Breaker Classes
- Capacitor Switching Class in Circuit Breaker Classes
- Mechanical Endurance Class in Circuit Breaker Classes
- Specific System Application Class in Circuit Breaker Classes
- Conclusion
Electrical Endurance Class in Circuit Breaker Classes
The electrical endurance class defines the ability of a circuit breaker to withstand electrical stress during operation. The term endurance refers to the capability to sustain hardship. In this context, it means handling electrical stresses such as short circuits and load switching. This class mainly focuses on the performance of the interrupting part of the circuit breaker.
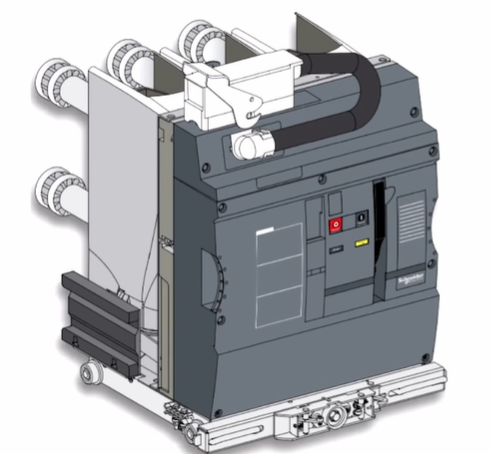
Electrical endurance class is divided into two categories:
- E1 class
- E2 class
E1 Class
The E1 class represents circuit breakers that require maintenance on the interrupting part during their service life.
In the early days of circuit breaker technology, regular maintenance was common, especially for contacts and interruptors. Because of this requirement, the E1 class was defined.
Any circuit breaker that does not qualify for E2 automatically falls under E1. This does not indicate poor quality. This means the breaker requires periodic maintenance during its life cycle.
E2 Class
The E2 class is known as the extended electrical endurance class. Circuit breakers in this class operate without requiring any major maintenance on the interrupting part throughout their entire service life. For example, if a breaker has a service life of 20 years, it does not need interruptor maintenance during that period.
However, some basic activities are still allowed, such as:
- Cleaning of components
- Gas refilling in gas-filled breakers, if leakage occurs
Major maintenance is not permitted. To qualify for the E2 class, breakers must pass strict tests without any maintenance. This requirement makes E2 class breakers superior to E1.
One important limitation applies here. Electrical endurance classes E1 and E2 apply only to circuit breakers rated from 1 kV to 52 kV. These classes are limited to distribution systems. IEC standards do not cover high voltage and extra-high voltage circuit breakers under this classification.
Capacitor Switching Class in Circuit Breaker Classes
The capacitor switching class defines how a circuit breaker behaves while switching capacitive or inductive loads. Switching these loads is more difficult than switching resistive loads because voltage and current are not in phase. There is a 90-degree phase difference between them. When voltage reaches zero, current becomes maximum, and when current is zero, voltage reaches its peak.
This behavior increases the risk of restriking during switching. Restriking can damage the circuit breaker and reduce its operational life. The capacitor switching class addresses this issue by defining how well a breaker can handle capacitive current interruption.
According to IEC 62271-100, capacitor switching class includes:
- C1 class
- C2 class
C1 Class
The C1 class indicates that the circuit breaker has a low probability of restriking during capacitive current switching. Breakers under this class pass specific tests that simulate capacitive load conditions. C1 class breakers are suitable for standard capacitive switching applications.
C2 Class
The C2 class represents a higher performance level. Circuit breakers under this class have a very low probability of restriking during capacitive switching. These breakers undergo more severe testing compared to C1 class breakers. Engineers consider C2 class breakers superior and prefer them in applications where capacitive switching is frequent or critical.
Mechanical Endurance Class in Circuit Breaker Classes
The mechanical endurance class focuses on the physical strength and durability of the circuit breaker. A circuit breaker is largely a mechanical device. It consists of moving parts such as springs, operating mechanisms, and linkages. These components must function reliably over many operations.

Mechanical endurance class tests how many no-load operations a circuit breaker can perform without major maintenance. This ensures long-term mechanical reliability.
Mechanical endurance is divided into:
- M1 class
- M2 class
M1 Class
In the M1 class, the circuit breaker must perform 2,000 no-load operations. During these operations, no major maintenance is allowed. The breaker must complete all operations successfully to qualify for this class.
M2 Class
The M2 class is the extended mechanical endurance class. In this case, the breaker must perform 10,000 no-load operations. This requirement is much higher than M1. The standard does not allow major maintenance during testing, but it permits minor activities such as greasing. Because M2 class breakers meet higher endurance demands, engineers consider them superior and suitable for applications that involve frequent operations.
Specific System Application Class in Circuit Breaker Classes
The specific system application class defines the suitability of a circuit breaker based on the type of network where it is installed. Circuit breakers are commonly used in cable networks and line networks. These systems create different transient recovery voltages across the breaker during operation.

Due to this difference, IEC defines two system application classes:
- S1 class
- S2 class
The S1 class indicates that the circuit breaker is suitable for cable networks. These systems produce a specific type of recovery voltage that the breaker must withstand. The S2 class indicates suitability for line networks, where recovery voltages behave differently.
Neither S1 nor S2 offers universal superiority. Each class serves a specific system type. Engineers select the class based on whether the breaker operates in a cable network or a line network.
This classification applies only to circuit breakers rated 100 kV and below. IEC standards do not include high voltage and extra-high voltage circuit breakers under this category.
Conclusion
Understanding what is circuit breaker classes is essential for selecting the correct breaker for a specific application. These classes clearly define electrical endurance, capacitive switching capability, mechanical strength, and system suitability. Each class is based on standardized testing and helps ensure safe and reliable system operation.
For a clearer and more practical understanding, it is strongly recommended to watch the full video explanation. The visual demonstration makes these concepts easier to grasp and apply in real systems.
- Posted In:
- Power System
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 8 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 240K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

