What are Advantages of HVDC Transmission?
What are Advantages of HVDC Transmission? https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/maxresdefault-1-1-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Janhavi Bhange Janhavi Bhange https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/073ecf147d16c491374b1228c7202e7f95ab7e88db921e3b1282760c074d7c00?s=96&d=mm&r=gHigh Voltage DC transmission is one of the most efficient methods to transmit electrical power. In recent years, discussions around HVDC have increased across the power sector. Many professionals now question whether HVDC will shape the future of electrical transmission.

To understand this shift, it is important to study the advantages of HVDC transmission in detail. This article explains those advantages clearly, following the same flow as the referenced explanation, while keeping the language simple and easy to understand.
Table of Contents
- Connecting Power Systems with Different Frequencies
- Precise Control of Power Flow
- Long-Distance Power Transmission Capability
- No Skin Effect in DC Transmission
- Lower Transmission Losses
- Bidirectional Power Flow Capability
- Improved Overall Energy Efficiency
- Environmental Benefits of HVDC Systems
- Suitability for Underground and Submarine Cables
- Role of HVDC in Modern Power Networks
Connecting Power Systems with Different Frequencies
The most important benefit of HVDC is its ability to connect power systems operating at different frequencies. In HVAC transmission, both systems must have identical frequencies.
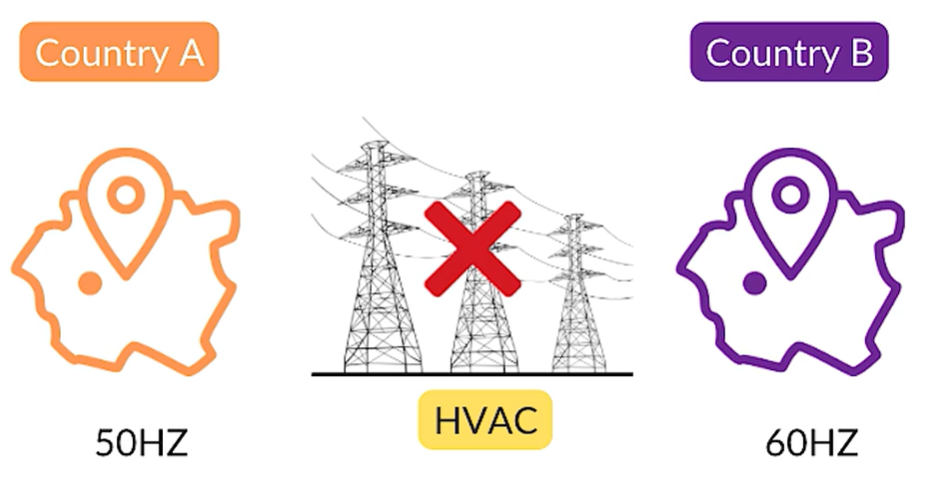
If the frequencies do not match, the connection becomes impossible. This creates a serious limitation when one country operates at 50 Hz and another operates at 60 Hz. HVDC solves this problem by converting AC power into DC power. DC does not have a frequency component. Its frequency is effectively zero.
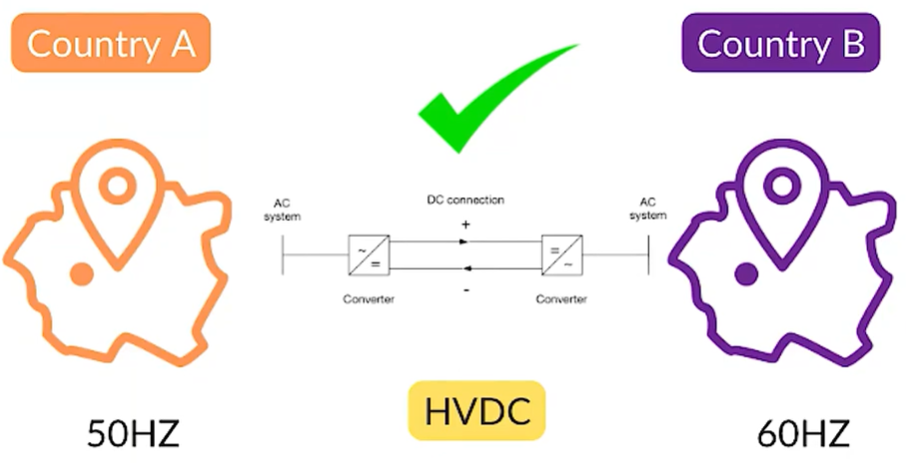
Because of this, frequency mismatch no longer restricts power transfer. As a result, two systems with different frequencies can be connected without difficulty. In many practical situations, HVAC cannot be used at all, making HVDC the only viable option.
Precise Control of Power Flow
Another key strength of HVDC lies in power flow control. In HVAC systems, power behaves like flowing water. It naturally chooses the path of least resistance. This often leads to uneven power distribution across the network, which can create stress and instability.
HVDC offers accurate control over power flow. Operators can decide how much power flows through the line and in which direction. This precise control helps stabilize the power system. It also allows better handling of sudden load changes. Because of this capability, HVDC plays an important role in improving overall system stability.
Long-Distance Power Transmission Capability
HVAC transmission faces technical limits over long distances. These limits arise due to inductance and capacitance in AC lines. As the distance increases, losses become significant. This restricts both the transmission length and the amount of power that can be sent.

HVDC does not face these constraints. Inductance and capacitance do not affect DC transmission. Only resistance plays a role. From a technical perspective, there is no strict limit on transmission distance or power capacity. Several existing projects already transmit large amounts of power over very long distances using HVDC. This makes HVDC highly suitable for long-distance power transfer.
No Skin Effect in DC Transmission
Skin effect is a major issue in AC systems. In HVAC transmission, current flows mainly along the surface of the conductor. This reduces effective conductor usage and increases resistance, leading to efficiency losses.

In DC transmission, skin effect does not exist. Current flows evenly across the entire conductor cross-section. This allows full utilization of the conductor diameter. As a result, thinner conductors can carry the same current more efficiently. Existing transmission lines also perform better when used for DC. The absence of skin effect improves overall system efficiency.
Lower Transmission Losses
Transmission losses are a major concern in power networks. HVAC systems experience high losses, especially as line length increases. Reactive components further contribute to these losses.
HVDC transmission significantly reduces these losses. Even when the length of the transmission line increases, the losses remain nearly constant. This ensures that more generated power reaches the receiving end. Reduced losses improve efficiency and reduce energy waste, making HVDC more economical over long distances.
Bidirectional Power Flow Capability
HVDC systems allow power to flow in both directions using back-to-back converter stations. Power can be transferred from one system to another and reversed when needed. This can be done using the same infrastructure, without adding new equipment.
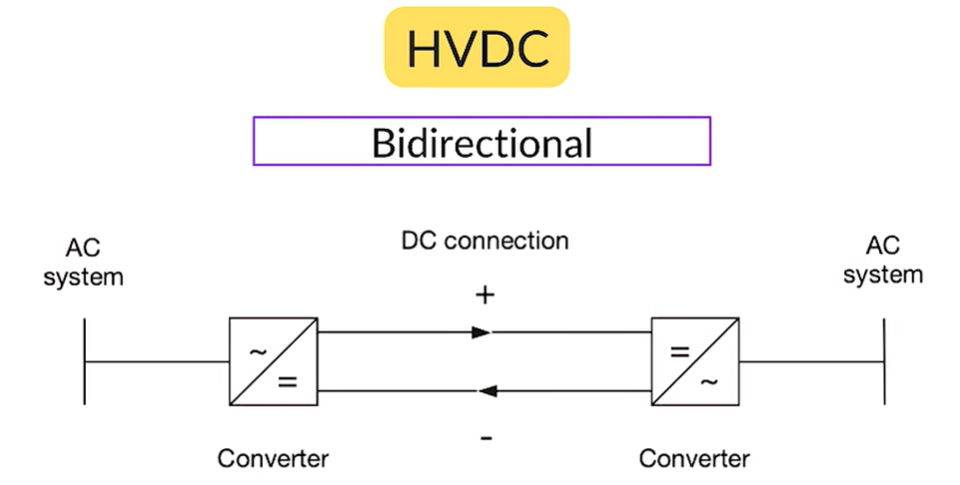
HVAC systems require additional arrangements to achieve similar flexibility. HVDC simplifies this process and provides better operational control. This bidirectional capability supports load balancing and improves system reliability.
Improved Overall Energy Efficiency
Lower transmission losses directly lead to higher energy efficiency. HVDC allows better utilization of generated power. More energy reaches consumers instead of being lost during transmission.
In contrast, HVAC systems lose a significant portion of power during transmission. HVDC reduces these losses and makes better use of existing infrastructure. Improved efficiency strengthens the entire power network and supports sustainable energy use.
Environmental Benefits of HVDC Systems
HVDC transmission also offers environmental advantages. HVDC towers have simpler designs compared to HVAC towers. They require less steel and occupy less land. This reduces construction material usage and minimizes land requirements.
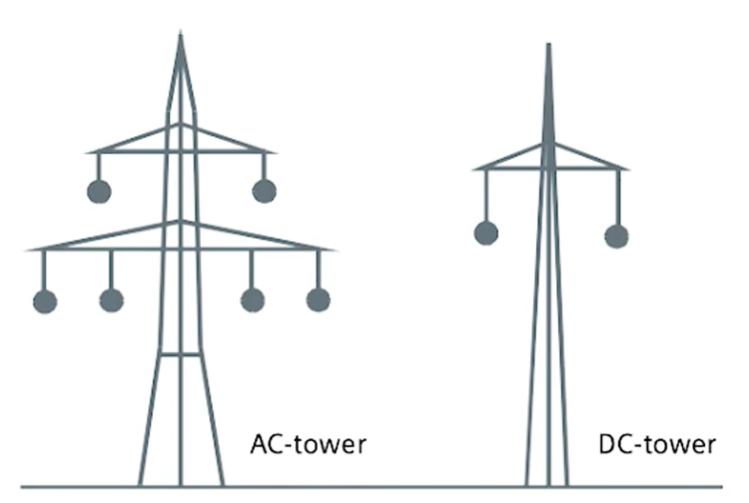
Better utilization of existing transmission corridors further reduces environmental impact. Fewer new towers are required, which helps preserve natural surroundings. Although HVDC is not completely impact-free, it performs better than HVAC in terms of environmental footprint.
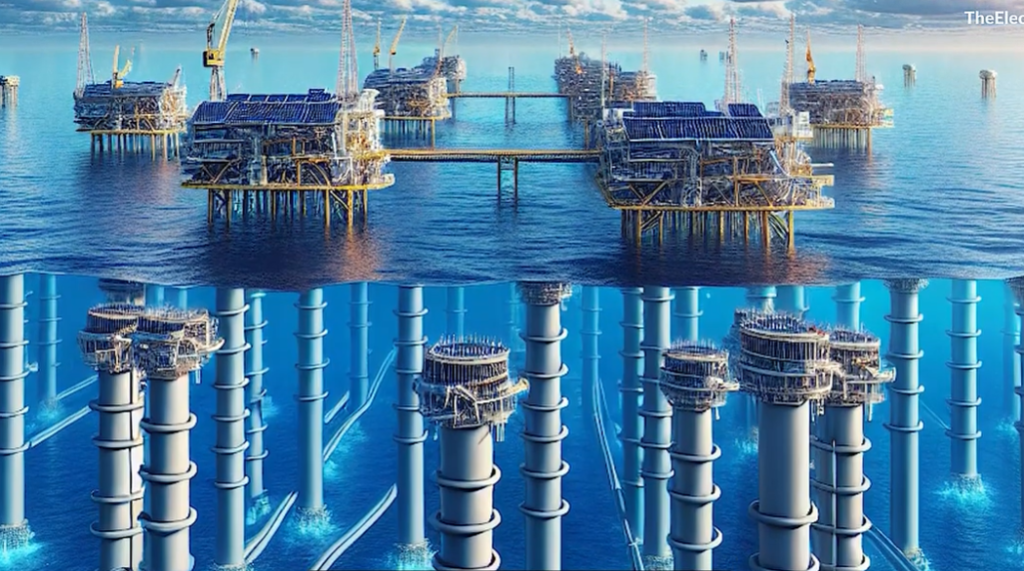
Suitability for Underground and Submarine Cables
Cables introduce additional challenges in power transmission. In HVAC systems, underground and submarine cables have high capacitance. This results in large charging currents, increased heating, and higher losses. These factors limit both cable length and power capacity.
HVDC transmission minimizes these issues. Capacitance effects remain low, and losses are significantly reduced. Transmission capacity remains stable even over long cable distances. Due to these advantages, many projects in Europe and North America use HVDC for submarine cable transmission.
Role of HVDC in Modern Power Networks
Modern power systems demand stability, flexibility, and efficiency. HVDC meets all these requirements. It supports interconnection between different systems, offers precise power control, enables long-distance transmission, and reduces losses.
It also improves environmental performance and supports reliable cable-based transmission. Together, these benefits highlight the growing importance of HVDC in modern power networks.
Conclusion
The advantages of HVDC transmission make it a strong solution for present and future power systems. It enables connections between different frequencies, provides precise power control, supports long-distance transmission, and reduces losses. It also improves energy efficiency, allows bidirectional power flow, lowers environmental impact, and works effectively with underground and submarine cables. For a clearer and more visual understanding of these points, watching the referenced video is strongly recommended.

- Posted In:
- HVDC


