HVAC vs HVDC: What is the Difference Between High Voltage AC and DC Transmission
HVAC vs HVDC: What is the Difference Between High Voltage AC and DC Transmission https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/maxresdefault-7-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gElectric power transmission mainly uses two methods today. The first method is High Voltage Alternating Current transmission, commonly known as HVAC. This is the most widely used transmission system across the world. The second method is High Voltage Direct Current transmission, known as HVDC, which is considered more efficient in specific scenarios. To clearly understand the difference HVAC vs HVDC, it is important to compare both systems using the same parameters and in a logical sequence.

This article explains the difference HVAC vs HVDC by following the exact flow used in the referenced video. Each comparison is explained in simple words, using short sentences and active voice for clarity.
Table of Contents
- HVAC vs HVDC for Transmission Between Different Frequencies
- HVAC vs HVDC for Power Transfer Capacity and Transmission Distance
- HVAC vs HVDC Conductor Diameter and Skin Effect
- HVAC vs HVDC System Structure
- HVAC vs HVDC Cost and Break Even Distance
- HVAC vs HVDC Power Flow Direction
- HVAC vs HVDC Transmission Losses
- HVAC vs HVDC Tower Design and Environmental Impact
- HVAC vs HVDC Summary
- Conclusion
HVAC vs HVDC for Transmission Between Different Frequencies
The first major difference HVAC vs HVDC appears when two power systems operate at different frequencies. Consider a situation where one country operates at 50 hertz and has surplus power available. The same country wants to export this power to a neighboring country that operates at 60 hertz.
With HVAC transmission, such a connection is not possible. One basic requirement for connecting two AC power systems is that both must operate at the same frequency. Since the frequencies differ in this case, HVAC cannot be used to connect the two systems.
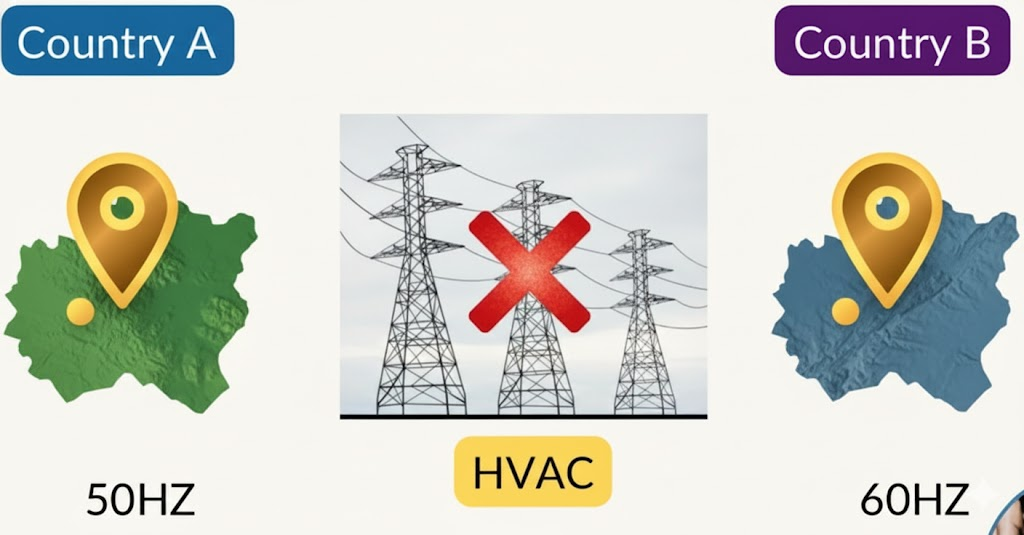
HVDC transmission solves this problem. In HVDC, frequency does not exist during transmission. The AC power from the first country is converted into DC using a converter station. This DC power is then transmitted to the second country. At the receiving end, another converter station converts DC back into AC at the required frequency. This makes HVDC the only option for connecting power systems operating at different frequencies.
HVAC vs HVDC for Power Transfer Capacity and Transmission Distance
Another important difference HVAC vs HVDC relates to power transfer capacity and distance. In AC systems, inductance and capacitance are unavoidable. These elements play a critical role in transmission lines and limit both the distance and capacity of power transfer.
As the transmission distance increases, losses also increase in HVAC systems. Heating issues further restrict how much power can be transmitted. Because of these limitations, very long HVAC transmission lines, such as 2,000 or 3,000 kilometers, are not practical.
In HVDC transmission, inductance and capacitance do not exist. Only resistance plays a role, following Ohm’s law. Due to this, HVDC does not face the same distance or capacity limitations. There are already HVDC transmission lines operating successfully over distances of more than 1,000 to 2,000 kilometers.
These issues become more severe in underground or submarine cables. AC cables suffer from strong capacitive effects, while HVDC avoids this problem completely. In such cases, HVDC becomes the preferred solution.
HVAC vs HVDC Conductor Diameter and Skin Effect
Conductor size highlights another key difference HVAC vs HVDC. In HVAC systems, current does not flow uniformly through the conductor. Instead, it concentrates near the surface due to a phenomenon called skin effect. This effect increases with frequency.
Because of skin effect, a large portion of the conductor remains unused in HVAC transmission. To carry the same amount of power, thicker conductors are required. This increases material usage and cost.
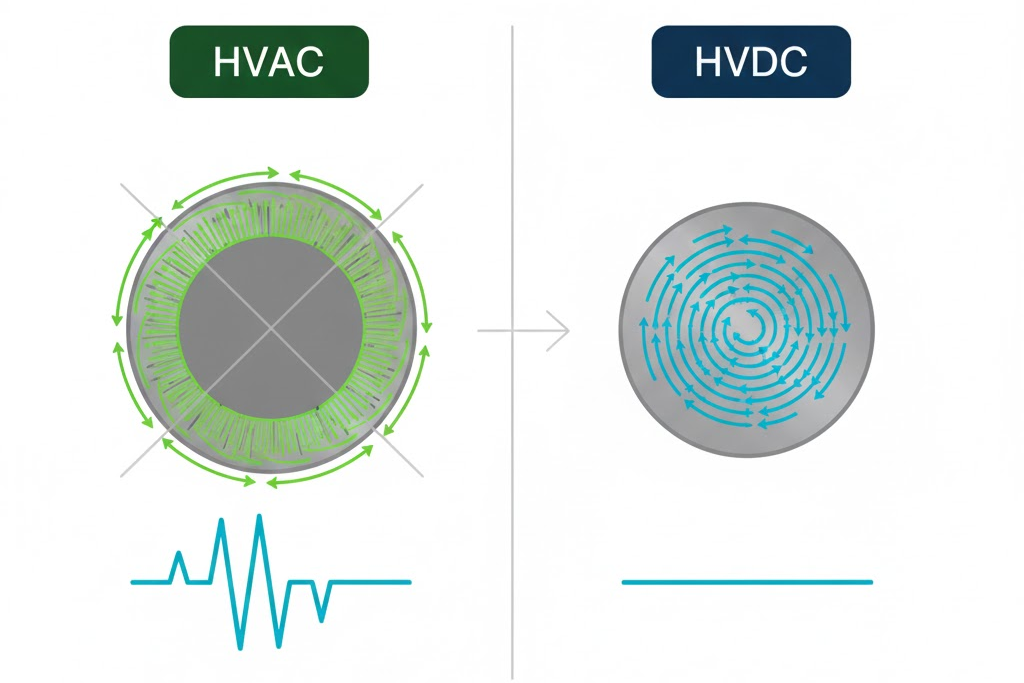
In HVDC transmission, frequency is absent, so skin effect does not occur. Current flows through the entire cross-section of the conductor.
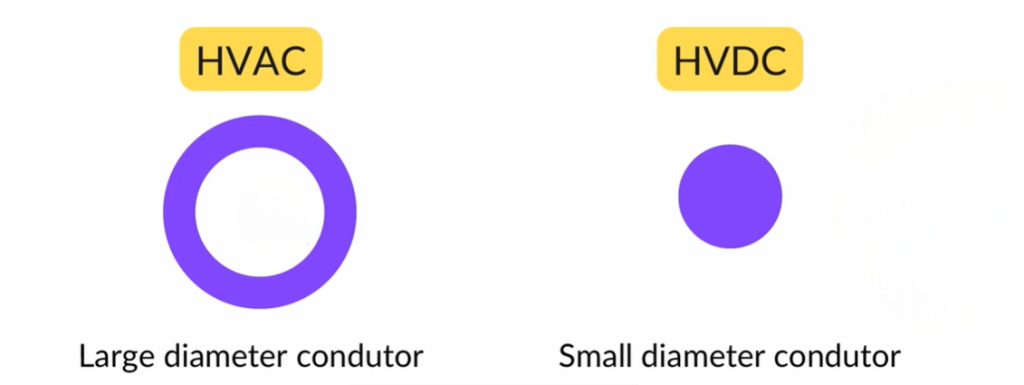
As a result, HVDC systems can use thinner conductors to transmit the same power. This directly affects conductor cost and efficiency.
HVAC vs HVDC System Structure
The system structure further explains the difference HVAC vs HVDC. HVAC systems have a simple and straightforward structure. Power plants generate electricity at a lower voltage. Step-up transformers then increase the voltage for transmission, and power flows through transmission lines.
HVDC systems have a more complex structure. The AC power first enters a converter station, where it is converted into DC. The DC power is transmitted over long distances. At the receiving end, another converter station converts DC back into AC before connecting to the AC transmission network.

Because of these additional components, HVDC systems are more complex in design and operation compared to HVAC systems.
HVAC vs HVDC Cost and Break Even Distance
Cost is a major factor when comparing HVAC vs HVDC. HVAC systems require lower initial investment. Substations, transformers, and related equipment are relatively less expensive.
HVDC systems involve high initial costs due to converter stations. In some cases, additional equipment such as reactive power compensation devices and AC harmonic filters are also required. These factors significantly increase the project cost.
To decide between the two systems, engineers calculate the break even distance. This distance represents the point where the total cost of HVAC and HVDC becomes equal. Below this distance, HVAC is more economical. Beyond this distance, HVDC becomes the better financial option. This analysis is done carefully before selecting the transmission method.
HVAC vs HVDC Power Flow Direction
Power flow direction also shows a clear difference HVAC vs HVDC. In HVAC systems, power flows in only one direction, from the source to the destination.
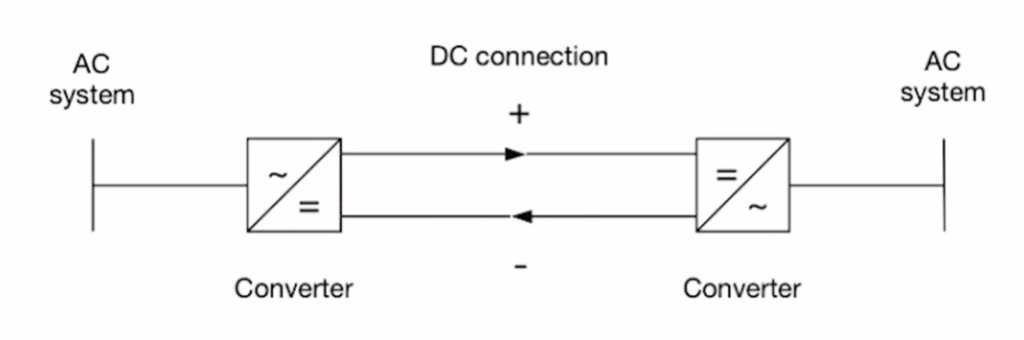
HVDC systems, especially back-to-back HVDC configurations, allow bidirectional power flow. Power can be transmitted from one AC system to another and also in the reverse direction using the same infrastructure. This flexibility is not possible in HVAC systems.
HVAC vs HVDC Transmission Losses
Transmission losses differ significantly in HVAC vs HVDC systems. HVAC systems experience higher losses due to inductance and capacitance. As transmission distance increases, these losses also increase.
In HVDC systems, losses depend only on resistance. Transmission losses remain nearly constant even when line length increases. Although converter stations introduce some losses, the overall losses in HVDC systems are still lower compared to HVAC systems.
HVAC vs HVDC Tower Design and Environmental Impact
Tower design further highlights the difference HVAC vs HVDC. HVAC transmission towers must carry three conductors. This makes the towers bulky and increases steel usage. The land requirement for HVAC towers is also higher.
HVDC towers carry only two conductors. This simplifies the tower design and reduces steel consumption. The land footprint is smaller, which improves environmental compatibility. Due to reduced material usage and land requirement, HVDC systems are more environmentally friendly than HVAC systems.
HVAC vs HVDC Summary
When comparing HVAC vs HVDC, several clear differences emerge. Connecting power systems operating at different frequencies is not possible with HVAC, but HVDC allows such connections. Distance and power transfer capacity also limit HVAC transmission, while HVDC operates without these constraints. Due to skin effect, HVAC needs thicker conductors, whereas HVDC can transmit power using thinner ones.
From a cost perspective, HVAC systems remain simpler and require lower initial investment. HVDC systems involve higher complexity and greater upfront cost. Once the break even distance is crossed, HVDC becomes the more economical choice. Power flow in HVAC remains unidirectional, while HVDC supports bidirectional transmission. Tower design also differs, with HVAC towers being bulky and HVDC towers offering a compact and more environmentally efficient structure.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference is essential for modern power transmission planning. Each system has its advantages and limitations. The choice depends on distance, cost, frequency requirements, and transmission needs. For a clearer visual explanation and deeper understanding, it is recommended to watch the referenced video, which explains these concepts step by step.

- Posted In:
- HVDC
- Power System
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 8 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 240K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

