
5 Problems Caused by Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads
5 Problems Caused by Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/maxresdefault-3-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gThree-phase systems are the backbone of modern power networks. They supply energy to industries, commercial buildings, and residential areas. Ideally, these systems should operate in a balanced condition. However, in real-world scenarios, balance is rarely achieved.
When a three-phase system becomes unbalanced, the effects are not minor. They impact equipment life, safety, efficiency, and overall system stability. Understanding these problems is critical for anyone dealing with electrical systems.
This article explains 5 problems caused by unbalanced 3-phase loads, following the same flow as the referenced video. The explanation starts with the basics of balance, moves to causes, and finally covers the impacts in detail.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Balanced and Unbalanced Loads in a 3-Phase System
- What Is a Balanced 3-Phase Load
- What Is an Unbalanced 3-Phase Load
- Causes of Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads
- 5 Problems Caused by Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads
- 5 Problems Caused by Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads
- Why Neutral Is Used in Distribution Systems
- Managing Problems Caused by Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads
- Conclusion
Understanding Balanced and Unbalanced Loads in a 3-Phase System
Many engineers assume that imbalance comes from the power source. In reality, this is incorrect. A three-phase source, such as a synchronous generator, produces perfectly balanced voltages. The windings are placed exactly 120 degrees apart. Frequency and voltage remain stable at the source end.
The real cause of imbalance is the load. Loads decide how much current flows in each phase. If the load is uneven, the system becomes uneven. A simple way to remember this is: sources create phases, while loads create balance.
An easy analogy is a truck. A truck is balanced by design. The imbalance happens when uneven cargo is placed inside it. Similarly, a power system becomes unbalanced due to how loads are connected and distributed.
What Is a Balanced 3-Phase Load
A balanced three-phase load exists when each phase has the same impedance. Impedance is the opposition offered to current in AC systems. When impedance is equal, current flowing through each phase is also equal.
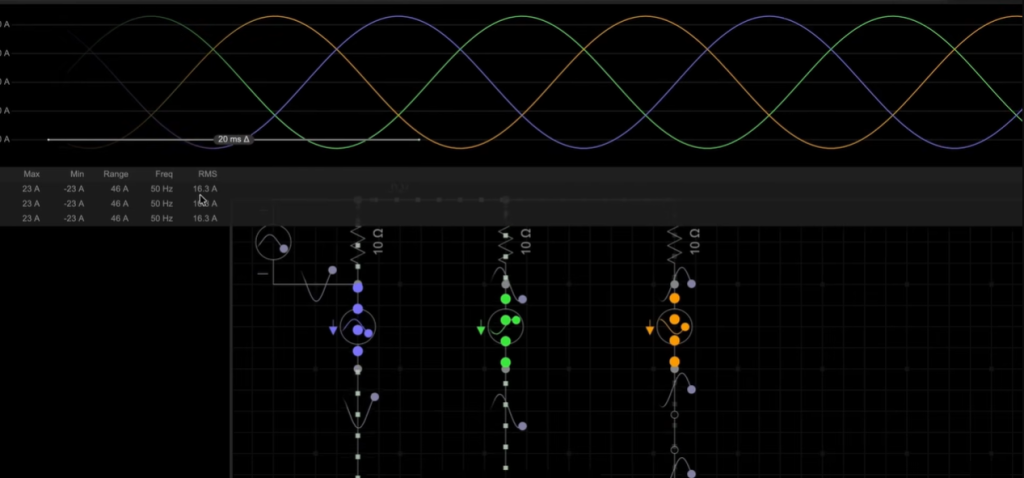
In a balanced condition, the current waveforms remain clean and sinusoidal. Phase angles stay correct, and the system behaves predictably. Voltage drop across each phase remains the same because the impedance values are identical.
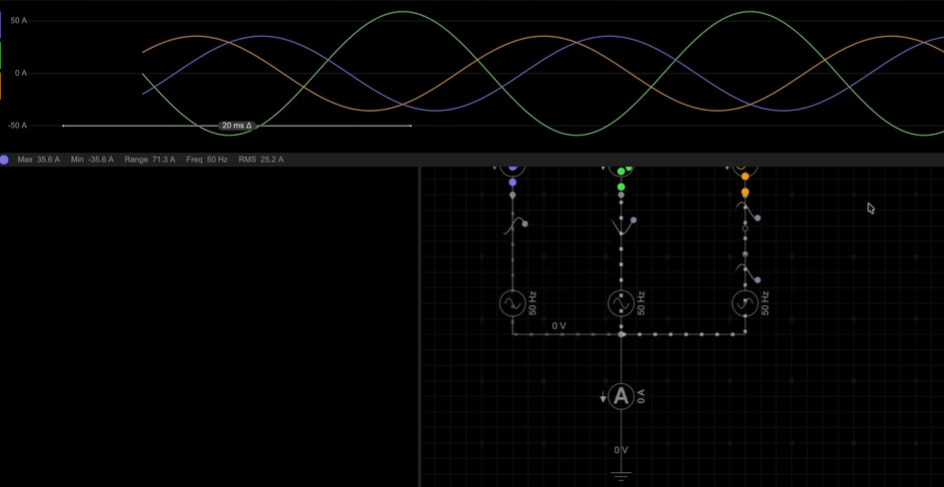
One of the most important features of a balanced load is neutral current. In this condition, the sum of the three phase currents at any instant is zero. Because of this, no current flows through the neutral conductor. Even if the neutral wire is removed, the system continues to operate normally.
This is why transmission systems do not require a neutral wire. Their loads remain largely balanced, and return currents cancel each other perfectly.
What Is an Unbalanced 3-Phase Load
An unbalanced load occurs when impedance differs across phases. Once this happens, current values also differ. Waveforms lose their shape, and phase angles shift away from their ideal positions.
Voltage drops across phases become unequal. Some phases may experience higher voltage, while others receive lower voltage. This uneven voltage supply creates serious risks for connected equipment.
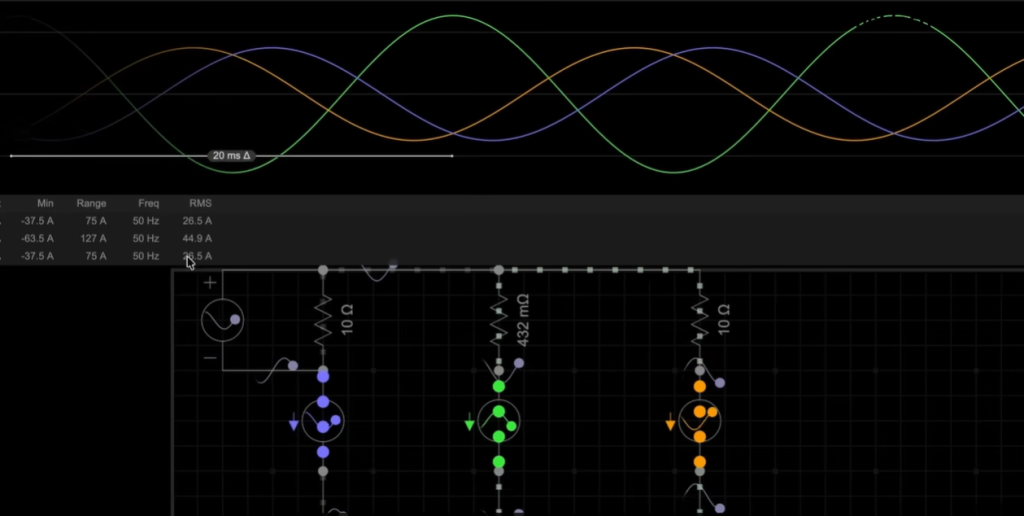
Unlike a balanced system, an unbalanced system carries current through the neutral conductor. The return currents no longer cancel each other. If the neutral wire is removed in this case, voltage imbalance becomes even worse.
This condition is most common in distribution systems. Unlike transmission systems, distribution networks serve a mix of single-phase and three-phase consumers. Perfect balance is practically impossible in such environments.
Causes of Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads
Several real-world factors create load imbalance. These causes often occur together and continuously affect the system.
Uneven Power Distribution in 3-Phase Loads
On the distribution side, power demand varies constantly. Industrial users consume large three-phase power. Residential users consume single-phase power. Even among homes, consumption differs from area to area.
Because of this variation, equal power distribution cannot be maintained. Some phases remain heavily loaded, while others remain lightly loaded. This uneven demand directly leads to unbalanced loads.
Unequal Impedance in Distribution Lines
Distribution lines do not always have equal lengths. One phase may travel a longer distance, while another takes a shorter route. This difference changes the impedance of each phase.
Unequal impedance leads to unequal current flow. Over time, this imbalance stresses the system. Manufacturing defects in motors can also cause imbalance. If motor windings have slightly different impedance values, the system becomes unbalanced during operation.
System Faults Causing Unbalanced Load Conditions
Faults can occur on both transmission and distribution sides. A single line-to-ground fault can disconnect one phase temporarily. During this time, the remaining phases carry additional load.
Although these faults may last only briefly, they still create unbalanced conditions. The sudden stress can damage equipment if protection systems fail to act quickly.
Harmonics and Nonlinear Loads
Modern electrical systems use many nonlinear loads. Computers and variable frequency drives do not draw current continuously. Instead, they draw current in pulses.
This behavior creates harmonics. Harmonics distort current waveforms and worsen imbalance. As harmonics increase, neutral current also increases, adding further stress to the system.
5 Problems Caused by Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads
Unbalanced loads create multiple issues that affect both equipment and the overall power system. Below are the five most critical problems.
Unequal Voltage Across Phases Due to Unbalanced Load
Unequal voltage is the most dangerous effect of an unbalanced load. Even if imbalance exists in only one phase, all three phases are affected. Voltage may rise in one phase and drop in another.
Most equipment is designed for a fixed voltage rating. When voltage exceeds this rating, insulation degrades faster. Over time, device lifespan reduces significantly.
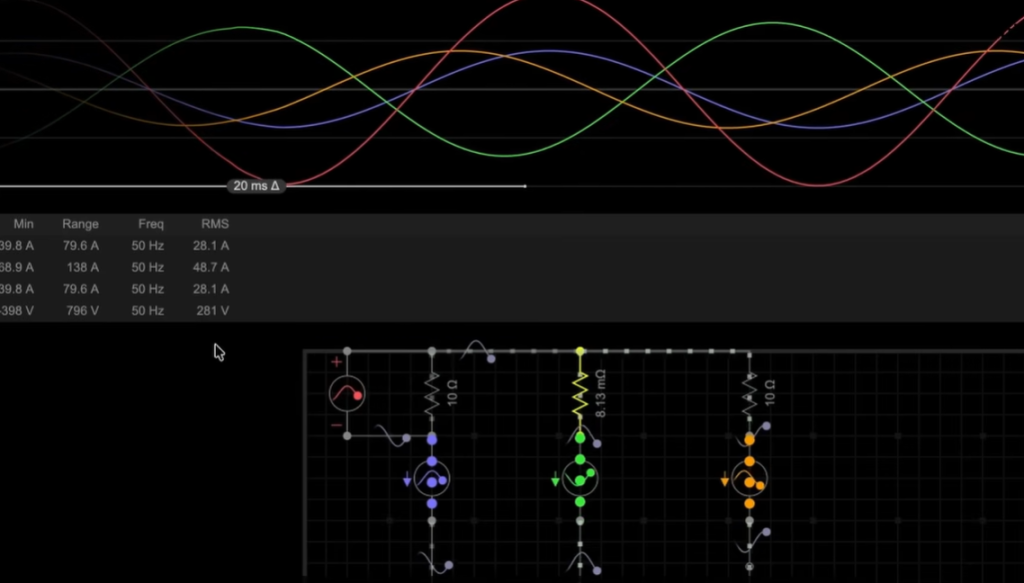
This issue is especially harmful for sensitive equipment. Motors, electronic devices, and control systems suffer long-term damage due to continuous voltage stress.
High Neutral Current in Unbalanced 3-Phase Systems
Neutral conductors are not designed to carry full load current. In many cables, the neutral has only half the capacity of phase conductors.
When a load becomes unbalanced, neutral current increases sharply. This causes overheating in the neutral conductor. Excess heat weakens insulation and increases the risk of short circuits or fire.
High neutral current is one of the most serious safety concerns in distribution systems and should never be ignored.
Increased Losses and Overheating Due to Load Imbalance
Unbalanced currents increase I²R losses in conductors. As current rises, losses increase rapidly. This extra loss converts directly into heat.
Overheating damages insulation and reduces equipment life. Transformers, cables, and switchgear all suffer under these conditions. Once overheating starts, it often leads to a chain reaction ending in failure.
Motor Issues Caused by Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads
Motors are highly sensitive to voltage imbalance. Unequal voltage creates uneven magnetic fields inside the motor. This results in vibration, noise, and reduced efficiency.
The motor draws more current to compensate, which increases heating. Over time, insulation breaks down, and the motor may fail prematurely. In severe cases, motors can burn out completely.
System Instability from Unbalanced Loads
Unbalanced loads disturb voltage, current, and neutral conditions across the system. This disturbance reduces overall system stability.
Protective devices may trip unnecessarily. Equipment may shut down without warning. If imbalance is not controlled, it can lead to partial or complete system failure.
Why Neutral Is Used in Distribution Systems
Transmission systems operate with balanced loads and controlled conditions. Neutral conductors are unnecessary there.
Distribution systems, however, serve varied consumers. Load imbalance is unavoidable. The neutral conductor helps manage return currents and stabilize voltages for single-phase users.
Removing neutral from an unbalanced system would worsen voltage imbalance and increase damage risk.
Managing Problems Caused by Unbalanced 3-Phase Loads
Although unbalanced loads cannot be fully avoided, their impact can be reduced. Reactive power control devices help stabilize voltage. Automatic power factor correction improves system performance.
For larger systems, energy storage solutions support voltage and frequency control. Harmonic controllers also reduce waveform distortion and neutral current.
Poor power factor caused by imbalance can lead to penalties from utilities. Managing balance improves both system health and operating cost.
Conclusion
Unbalanced loads are a reality of modern power systems. While they cannot be eliminated completely, their effects can be controlled with proper understanding and corrective measures.
The 5 problems caused by unbalanced 3-phase loads affect voltage, current, equipment life, and system stability. Ignoring these issues increases risk and cost.
For a clearer and visual explanation of these concepts, it is strongly recommended to watch the referenced video, which demonstrates these effects step by step for better understanding.

- Posted In:
- Power System
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 9 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 250K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

