
Understanding Power System Stability
Understanding Power System Stability https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/maxresdefault-2-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gUnderstanding Power System Stability often feels complex at first. Many learners think it needs heavy math. In reality, the concept is simple. Everything depends on how it is explained. When the basics are clear, the idea becomes easy to remember.
This article explains Understanding Power System Stability using a simple car analogy. The focus stays on concepts, not equations. The goal is clarity. By the end, the idea of stability will feel natural and logical.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Power System Stability Using a Simple Car Analogy
- Balance, Disturbance, and Balance in Power Systems
- What Is Power System Stability in Simple Terms
- Key Parameters Used to Judge Power System Stability
- Disturbances Faced by Power Systems
- Power System Stability as a Recovery Capability
- Synchronism and Power System Stability
- Why Understanding Power System Stability Is Important
- Different Levels of Disturbances in Power Systems
- Types of Power System Stability
- Why Disturbances Cannot Be Avoided
- Methods Used to Improve Power System Stability
- New Challenges in Power System Stability
- Conclusion
Understanding Power System Stability Using a Simple Car Analogy
To understand power system stability, imagine driving a car on a highway. The car moves at a constant speed. The road is smooth. Everyone inside the car feels comfortable. At this point, the car is balanced and stable.

This situation does not last forever. After some time, the road conditions change. A speed breaker or a pothole may appear ahead. When the car hits it, the smooth motion gets disturbed. To manage this, you slow down the vehicle. You also adjust the gear and control the steering to absorb the shock.

Once the disturbance passes, the road becomes smooth again. The car returns to a steady speed. The passengers feel comfortable once more. The car is back to its balanced state.
This simple cycle explains power system stability very well.
Balance, Disturbance, and Balance in Power Systems
The car starts in a balanced condition. Then a disturbance appears. After adjustments, balance returns. This same pattern applies to power systems.
A power system normally operates in a balanced state. Then a disturbance occurs. If the system can return to normal operation after the disturbance, it is considered stable.
This idea forms the foundation of Understanding Power System Stability. Disturbances cannot be avoided. What matters is how well the system recovers after them.
What is Power System Stability in Simple Terms
Power system stability is the ability of an electrical power system to return to its normal operating condition after a disturbance.
A disturbance can occur due to several reasons. Common causes include electrical faults and sudden load changes. In some cases, generator failure can also trigger instability.
If the system regains normal frequency, voltage, and phase balance after the disturbance, it is stable. If it fails to do so, instability occurs.
Key Parameters Used to Judge Power System Stability
To determine whether a power system is stable, engineers monitor three key parameters. These parameters indicate whether the system remains balanced.
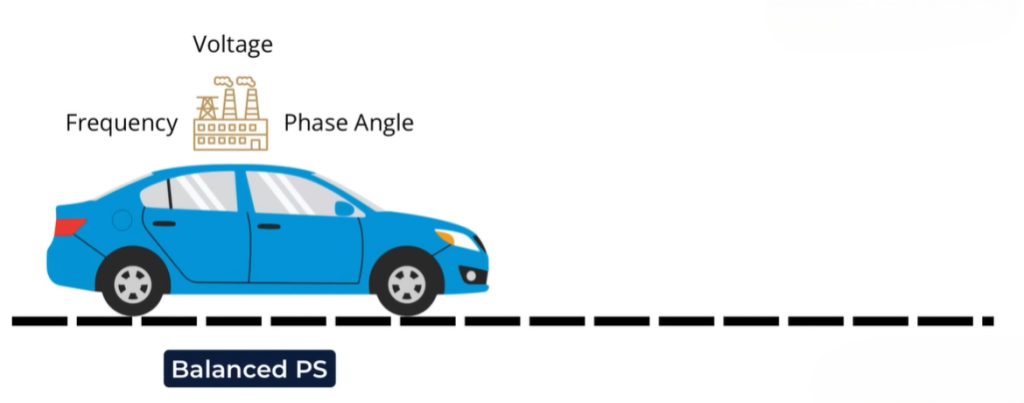
Frequency Stability in Power Systems
Frequency is the first and most important indicator. A stable power system operates at a constant frequency, usually 50 Hz or 60 Hz.
All synchronous machines in the system rotate at the same speed. This shared speed keeps the frequency constant across the network. When the speed changes, frequency also changes. That change signals a disturbance in the system.
Voltage Stability and Power Quality
Voltage is the second key indicator. Electrical devices are designed to operate at specific voltage levels. If the voltage stays within those limits, the system remains stable.
When voltage fluctuates beyond limits, instability occurs. Such fluctuations can damage equipment and affect performance.
Phase Angle Balance in Three-Phase Systems
Power systems use three-phase electricity. In such systems, phase angle balance is critical. Along with frequency and voltage, phase angle must stay within acceptable limits.
If all three parameters remain stable, the power system is considered balanced.
Disturbances Faced by Power Systems
Just as roads have potholes and speed breakers, power systems face disturbances. However, these disturbances take different forms.
A generator may trip. Similarly, a transmission line may fail. At times, a large load may suddenly connect or disconnect. In other cases, the excitation system may malfunction. As a result, all these events disturb key system parameters.
Because of these disturbances, frequency, voltage, or phase angle can deviate from normal values. In real-world power systems, such events are unavoidable. Therefore, system stability depends on how effectively and how quickly the system responds after these disturbances occur.
Power System Stability as a Recovery Capability
After a disturbance, the system temporarily enters an unstable condition. Parameters move away from normal values.
If the system can restore these parameters and return to steady operation, stability exists. This recovery ability defines power system stability.
The simple rule remains the same: balance, disturbance, and balance again.
Synchronism and Power System Stability
The term synchronism appears frequently when discussing stability. Synchronism means that all generators rotate together at the same speed.
Stability and synchronism are closely related. In many cases, these terms are used interchangeably. When machines remain in synchronism after a disturbance, the system stays stable.
Loss of synchronism leads to instability and possible system collapse.
Why Understanding Power System Stability Is Important
Some consumers may feel stability does not concern them. They only want electricity at the socket. However, instability affects everyone.
Unstable power systems lead to unreliable supply. Voltage fluctuates frequently. Power interruptions become common. This situation feels like driving constantly on a damaged road.
Electrical equipment also suffers due to instability. Household appliances, industrial machines, and substation equipment are designed for specific voltage levels. Continuous fluctuations reduce their lifespan and increase failures.
In critical applications, instability becomes dangerous. Medical equipment depends on steady power. Fluctuating supply can put human lives at risk.
The most severe consequence of instability is a blackout. In today’s world, electricity supports every aspect of life. Blackouts disrupt communication, healthcare, transport, and industry. For any country, stable electricity is essential for development.
Different Levels of Disturbances in Power Systems
Not all disturbances have the same impact. Some are small and gradual. Others are sudden and severe.
Similarly, some roads have small bumps, while others have deep potholes. Power system stability is classified based on the type of disturbance faced by the system.
Types of Power System Stability
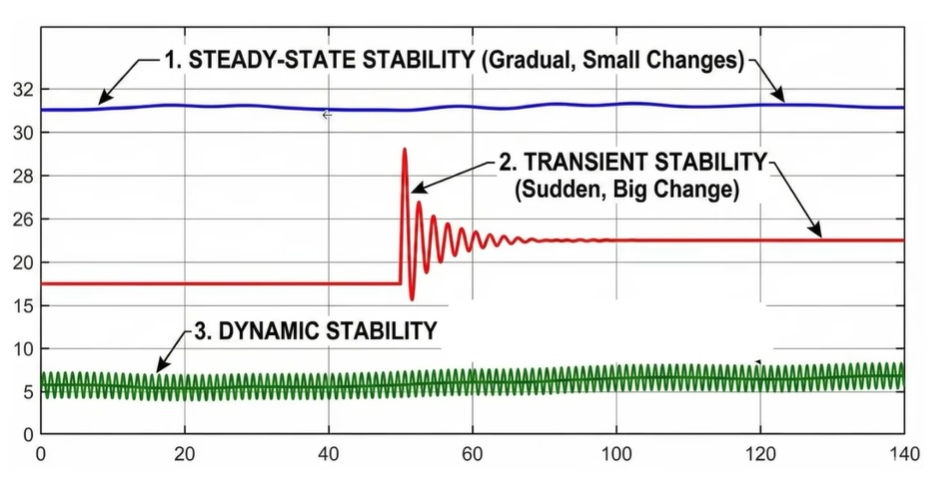
Steady State Stability in Power Systems
Steady state stability deals with small and slow disturbances. These changes occur gradually and do not involve sudden shocks.
A common example is daily load variation. During night hours, load decreases slowly. During daytime, load increases gradually. The power system must adjust to these changes without losing balance.
The ability to handle such slow variations defines steady state stability.
Transient Stability in Power Systems
Transient stability deals with sudden and large disturbances. These events occur without warning and have significant impact.
Examples include sudden generator failure or abrupt disconnection of a large load. Such events cause sharp changes in system conditions.
Although these disturbances last for a short time, they are critical. The system must remain in synchronism during and after the event. The ability to survive such sudden shocks defines transient stability.
Dynamic Stability After Transient Events
Dynamic stability comes into focus after transient stability. Once the major disturbance is cleared, small oscillations remain in the system.
These oscillations appear as small fluctuations in frequency or power flow. The system must damp these oscillations over time.
A system may handle transient disturbances but fail to control dynamic oscillations. Therefore, dynamic stability is equally important.
Why Disturbances Cannot Be Avoided
Disturbances in power systems are inevitable. Equipment ages. Weather affects infrastructure. Loads change constantly.
Just as roads cannot always be smooth, power systems cannot always remain disturbance-free. The focus should be on minimizing impact and ensuring fast recovery.
Methods Used to Improve Power System Stability
Several techniques help power systems recover quickly after disturbances.
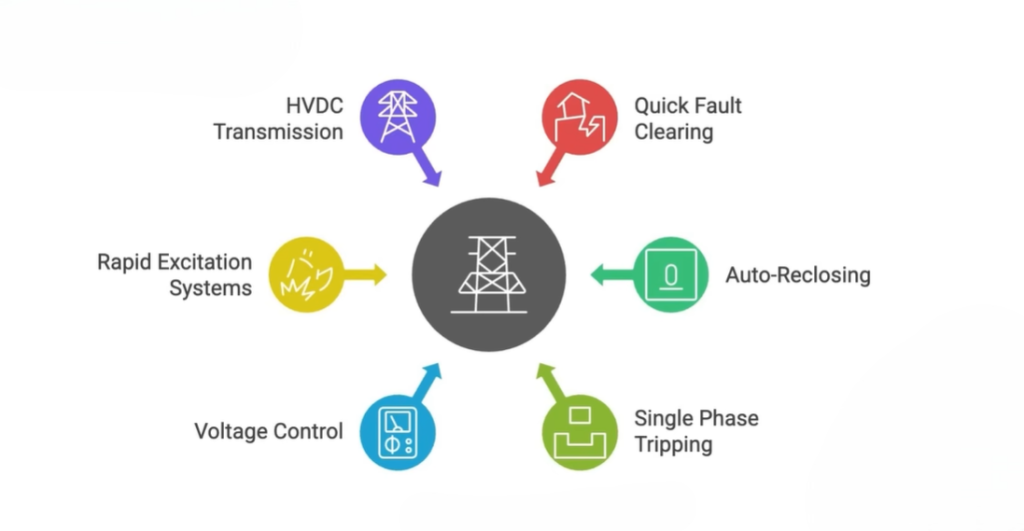
Common stability improvement methods include:
- Fast fault detection and clearing using relays and circuit breakers
- Auto reclosing to restore supply after temporary faults
- Single-phase tripping to isolate only the faulty phase
- Voltage control using reactors, capacitors, and control devices
- Rapid excitation systems for synchronous generators
- HVDC transmission for precise power flow control
These methods reduce disturbance duration and improve system recovery.
New Challenges in Power System Stability
Modern power grids are changing rapidly. Renewable energy sources are being added in large numbers. Their output is not always constant.
This integration reduces system inertia. Voltage control becomes more difficult. Reactive power support decreases.
These changes introduce new challenges for maintaining power system stability.
Conclusion
Understanding Power System Stability becomes simple when explained clearly. The car analogy helps visualize balance, disturbance, and recovery. This article follows the same flow as the original explanation, making the concept easy to grasp and remember.
For an even clearer and more visual understanding, it is strongly recommended to watch the video linked above, as it reinforces every concept explained here in a simple and effective manner.

- Posted In:
- Power System
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 9 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 250K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

