
What are Disadvantages of HVDC Transmission
What are Disadvantages of HVDC Transmission https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/maxresdefault-2-1-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gHVDC transmission provides several technical advantages, but it also brings critical drawbacks. These disadvantages mainly affect cost, power quality, system complexity, and long-term maintenance. Understanding these limitations is essential before selecting HVDC for power transmission. This article explains the disadvantages of HVDC transmission in the same sequence and logic as discussed in the referenced video.
Table of Contents
- Conversion Requirement and Converter Stations
- Power Quality Issues Due to Current Source Converters
- Voltage Dependency and Operational Risk
- Converter Transformers and Noise Issues
- Large Land Requirement for HVDC Stations
- Need for Skilled Manpower and Regular Maintenance
- High Initial Cost of HVDC Transmission
- Challenges in HVDC Switchgear and Circuit Breakers
- Shorter System Life and Refurbishment Needs
- Conclusion
Conversion Requirement and Converter Stations
One of the biggest disadvantages of HVDC transmission is the need for power conversion. Electrical networks operate on AC power. HVDC transmission cannot connect directly to these networks. First, the incoming AC power must convert into DC. When the power reaches the receiving end, DC must convert back into AC before connecting to the grid.
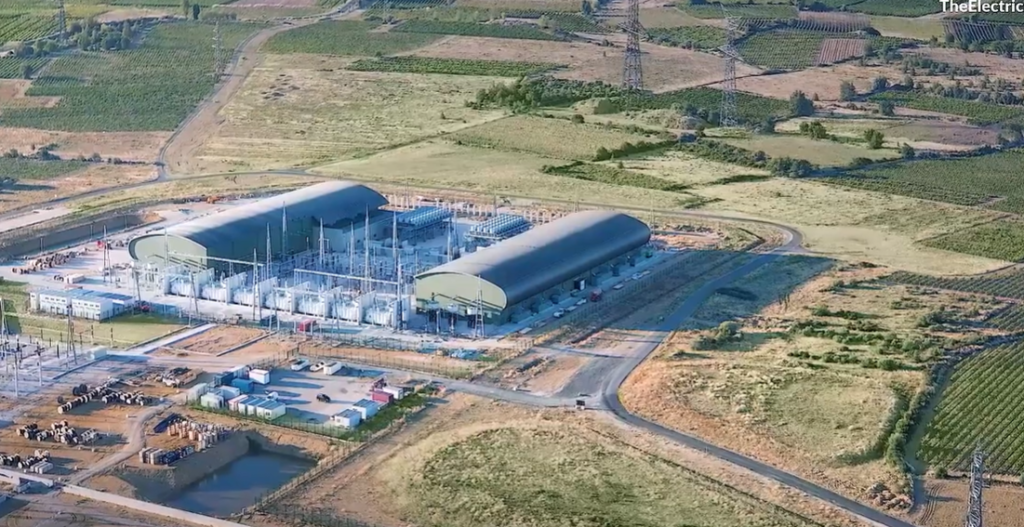

This conversion process requires dedicated converter stations at both ends. These stations are not optional. They form a critical part of the HVDC system. Building converter stations increases system complexity. It also raises the initial project cost significantly. Without these stations, HVDC transmission cannot function.
Power Quality Issues Due to Current Source Converters
To convert AC into DC, HVDC systems commonly use the current source converter method. This method creates serious power quality problems. During conversion, the system absorbs reactive power from the surrounding AC network. At the same time, it generates harmonic currents.
Both reactive power absorption and harmonic generation disturb power quality. Poor power quality affects voltage stability and system performance. Such conditions are unacceptable in power networks. Therefore, corrective measures become mandatory.
To improve power quality, the system requires additional equipment, such as:
- Reactive power compensation devices
- AC harmonic filters
These components are essential for stable operation. However, they increase system size and cost. As a result, the overall HVDC project becomes more expensive.
Voltage Dependency and Operational Risk
Another major disadvantage of HVDC transmission lies in voltage dependency. In current source converters, the output depends directly on the incoming voltage. If the input voltage fluctuates, the output also changes. This behavior creates operational risk.
Voltage fluctuations can cause incorrect converter operation. In some cases, converters may fail to function properly. To avoid such issues, the input voltage must remain stable at all times. This requirement demands strict system control.
Voltage source converters can reduce this dependency. However, this technology is still under development. It is not fully mature. Due to this limitation, most systems still rely on current source converters. Therefore, voltage dependency remains a concern in many HVDC projects.
Converter Transformers and Noise Issues
HVDC systems also require converter transformers. These transformers adjust voltage levels to values suitable for the converters. They also shift phase angles. Unlike standard three-phase systems with 120-degree separation, HVDC systems may use angles such as 50 degrees or 150 degrees.
While converter transformers perform essential functions, they introduce another drawback. During operation, they generate significant noise. This noise can create environmental and operational challenges. In some locations, noise control measures become necessary, adding further cost.
Large Land Requirement for HVDC Stations
HVDC converter stations require a large amount of land. These stations include both indoor and outdoor equipment. In addition, reactive power compensation units and harmonic filters need extra space.
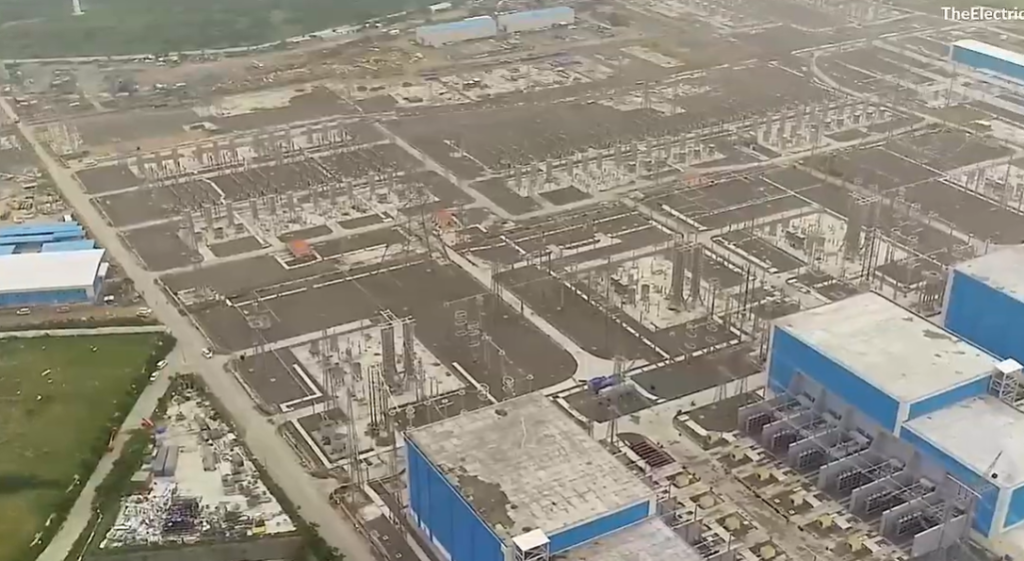

When all components are considered together, the land requirement becomes very high. Finding suitable land becomes difficult, especially near urban areas. Land acquisition increases project cost and can delay execution. This large spatial requirement is a clear disadvantage of HVDC transmission.
Need for Skilled Manpower and Regular Maintenance
HVDC systems demand highly skilled manpower. Converter stations are critical and complex. Their installation, operation, and maintenance require trained professionals. Skilled personnel come at a higher cost, which increases operational expenses.
Maintenance requirements further add to the challenge. HVDC systems need regular and careful maintenance. Unlike HVAC systems, which are more robust, HVDC systems cannot operate with minimal supervision. Maintenance tasks must be handled only by skilled workers because the equipment is expensive and sensitive.
In addition, HVDC projects require a large inventory of spare parts. Many components are critical. If a failure occurs, immediate replacement is necessary. Maintaining spares increases storage and management costs. All these factors raise the overall project expense.
High Initial Cost of HVDC Transmission
When all disadvantages are combined, the most visible issue becomes cost. HVDC transmission has a very high initial investment. Converter stations, transformers, filters, compensation devices, skilled manpower, and maintenance infrastructure all contribute to this cost.
Although HVDC can become economical over long distances, the initial project cost remains significantly high. A detailed break-even analysis is necessary before selecting HVDC. In many scenarios, the high upfront cost limits its feasibility.
Challenges in HVDC Switchgear and Circuit Breakers
HVDC switchgear presents another serious challenge. Circuit breakers in HVDC systems are difficult to design and manufacture. In HVAC systems, current naturally reaches zero every half cycle. Circuit breakers take advantage of this natural current zero to interrupt the arc.
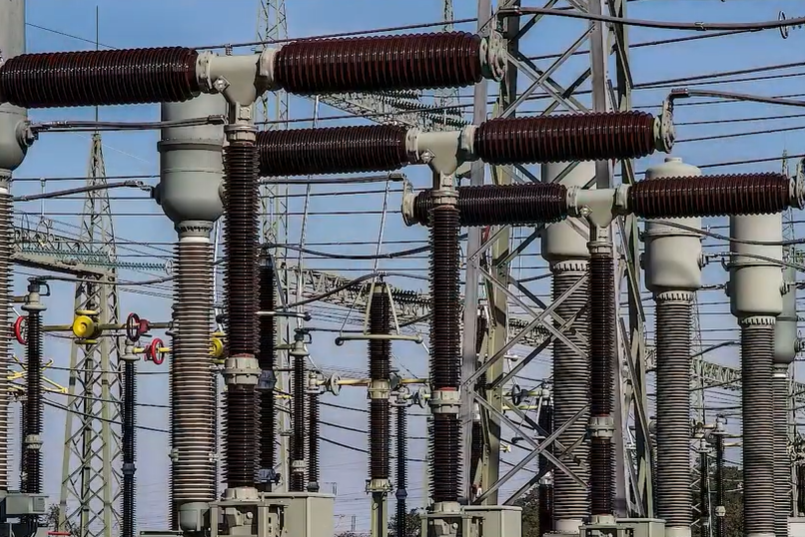

In HVDC systems, current never reaches zero naturally. Therefore, the system must force the current to zero artificially. This process is complex and requires advanced technology. As a result, HVDC circuit breakers become expensive and technically demanding.
Although HVDC circuit breakers are available, their construction and operation remain critical. Their cost further adds to the overall expense of HVDC transmission systems.
Shorter System Life and Refurbishment Needs
Another disadvantage of HVDC transmission is its shorter lifespan. HVAC systems typically last between 60 and 80 years, especially overhead lines. They require minimal refurbishment over their lifetime.
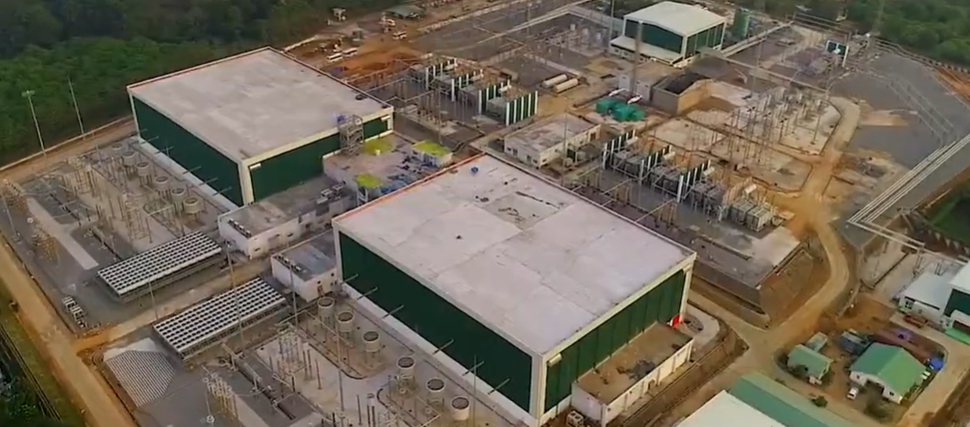

In contrast, HVDC systems have an expected life of around 40 years. Some converter station components may need replacement or refurbishment within just 20 years. These replacement costs must be considered during project planning. Over time, refurbishment expenses increase the total cost of ownership.
Conclusion
HVDC transmission offers many technical benefits, but its disadvantages are significant. The need for conversion stations, power quality issues, voltage dependency, large land requirements, skilled manpower, frequent maintenance, complex switchgear, high initial cost, and shorter lifespan all affect feasibility. Engineers must carefully study these factors before choosing HVDC transmission.
For a clearer and more practical understanding of these limitations, it is recommended to watch the video explanation, as it visually connects all concepts discussed above.

- Posted In:
- HVDC
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 8 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 240K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

