How Generators Keep Voltage Stable
How Generators Keep Voltage Stable https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/maxresdefault-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gStable voltage is something we often take for granted. Lights turn on, machines run, and appliances work without sudden dimming or surging. Yet, behind this calm output lies a system that handles constant changes in load. Generators must respond to these changes at every moment, and they do this with the help of excitation control. Before we get into the technical parts, it helps to know why voltage needs constant control and how generators manage it so smoothly.
Table of Contents
- Why We Need Excitation Control to Keep Voltage Stable
- How Faraday’s Law Helps Us Keep Voltage Stable
- Why We Cannot Change Coil Turns or Rotor Speed
- Why Generators Use Electromagnets to Keep Voltage Stable
- How Reactive Power Control Helps Keep Voltage Stable
- Why We Need Automatic Voltage Regulators to Keep Voltage Stable
- DC Excitation System and How It Helps Keep Voltage Stable
- AC Brushless Excitation System and How It Keeps Voltage Stable
- Static Excitation System and How It Keeps Voltage Stable
- Summary of How Generators Keep Voltage Stable
- Conclusion
Why How Generators Keep Voltage Stable Matters
The voltage in our homes or factories stays almost constant every day. It does not drop or rise much even when the load changes. This happens because many voltage control tools work quietly in the background. One of the most important methods is the generator excitation system.
It helps the generator hold the right voltage across different load levels. In this guide, we look at How Generators Keep Voltage Stable by using excitation control. First, we see why generators need excitation. Then, we explore the methods that help keep the voltage steady.
How Faraday’s Law Helps Us Keep Voltage Stable
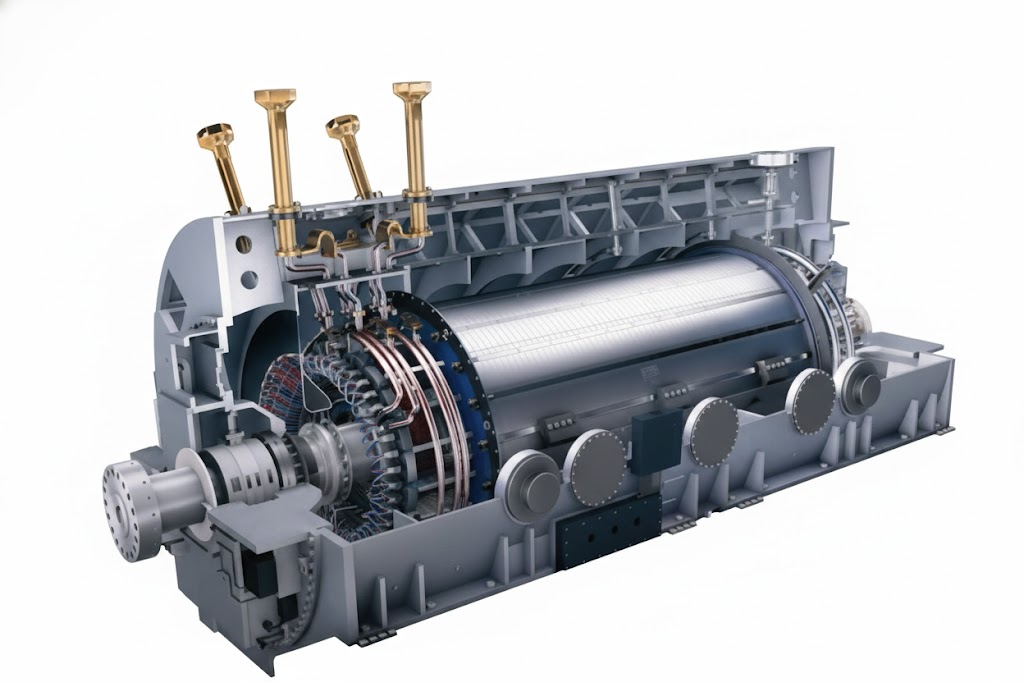
At the center of every power plant, we have a synchronous generator. This generator produces electricity through Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. This law forms the core of voltage control.

Faraday’s law says a conductor gets a voltage when it cuts a magnetic field. This can happen in two ways. You can rotate the magnetic field. Or you can rotate the conductor. Both ways induce a voltage.
The induced voltage depends on two things. It depends on the number of turns in the coil. It also depends on how fast the magnetic field changes.
This gives us two possible methods to control the voltage:
- Change the number of turns in the conductor.
- Change the magnetic field strength.
Both can change the induced voltage.
Why We Cannot Change Coil Turns or Rotor Speed
In large generators, we cannot change the number of turns. These machines are already built. The coil design is fixed. So this option is not useful.
The next option is to change the magnetic field. You can do this by changing the rotor speed. Or you can change the strength of the magnetic field.
But rotor speed is also fixed. The rotor speed decides the grid frequency. If you change speed, the frequency changes. This leads to more problems. So we do not adjust speed. Generators run at constant speed to keep frequency constant at 50 Hz or 60 Hz.
This means the only valid way to control voltage is to change the magnetic field intensity. We do this by adjusting the excitation.
Why Generators Use Electromagnets to Keep Voltage Stable
You can create a magnetic field using a permanent magnet or an electromagnet. But you cannot control a permanent magnet easily. So generators use electromagnets. They need a DC supply to create the magnetic field.
If you control this DC supply, you can control the magnetic field. And when you control the magnetic field, you also control the voltage. This is why excitation is essential for every synchronous generator.
The power system is dynamic. The load keeps rising and falling. So the voltage also keeps shifting. If the load increases, voltage drops due to losses in generators and transformers. If the load decreases, voltage rises due to the Ferranti effect.
This is why excitation must change with load.
How Reactive Power Control Helps Keep Voltage Stable
Voltage control in a power system depends on reactive power. This is a key point. When you control reactive power, you control voltage. Many devices help manage reactive power. Examples include capacitor banks and shunt reactors.
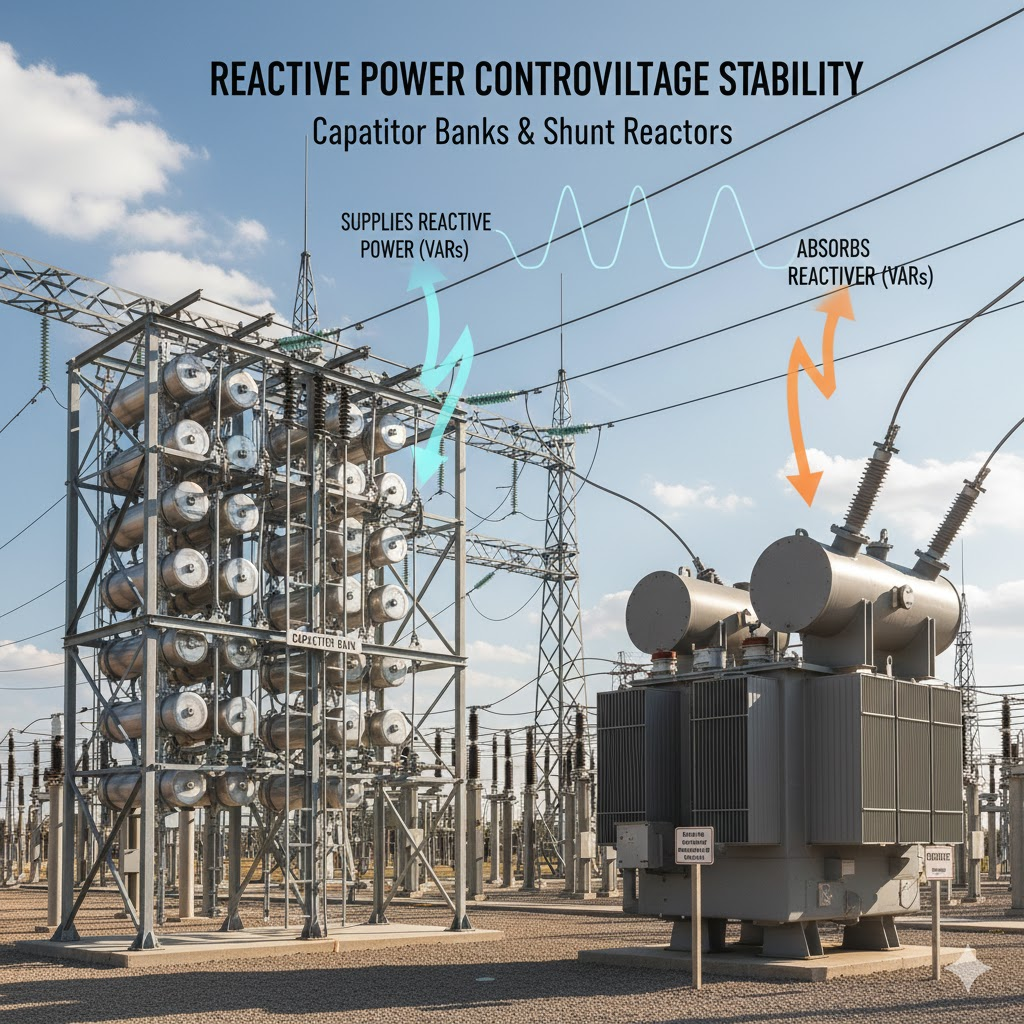
A shunt reactor consumes reactive power when the voltage rises. A capacitor bank adds reactive power when the voltage drops.
Generators also play a major role here. They do not only supply active power. They also supply reactive power. This reactive power builds magnetic fields in motors and transformers.
So when we change generator excitation, we directly change reactive power output. When the load rises, the system needs more reactive power. So we increase excitation. When the load falls, we reduce excitation.
This is how generators keep voltage stable in every operating condition.
Why We Need Automatic Voltage Regulators to Keep Voltage Stable
We cannot adjust excitation by hand. The load changes all the time. Voltage changes all the time. So we need a device that adjusts excitation on its own. This device is the Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR).

The AVR is the control brain of the excitation system.
It works like this:
- We set a target voltage.
- The AVR measures the generator terminal voltage.
- If the voltage drops, the AVR increases excitation.
- If the voltage rises, the AVR reduces excitation.
In this way, it keeps the voltage stable even when the system load changes.
Behind the AVR, we have the complete excitation system. The excitation system delivers and controls the DC field current. Different generators use different types of excitation systems.
DC Excitation System and How It Helps Keep Voltage Stable
The oldest type of excitation is the DC excitation system. Here, a DC generator supplies the excitation current. If you change the DC current, you change the magnetic field. This then changes the voltage.
This method works, but it needs brushes and slip rings. It also has high maintenance needs.
AC Brushless Excitation System and How It Keeps Voltage Stable
A brushless AC excitation system came later. It solved many maintenance problems. It uses an AC exciter mounted on the same shaft as the main generator.
Here is how it works:
- The AC exciter makes AC.
- A rotating rectifier changes AC to DC.
- This DC goes to the main generator field winding.
This system removes the need for brushes. It is clean and needs less maintenance. It also improves reliability. That is why many modern generators use brushless excitation.
Static Excitation System and How It Keeps Voltage Stable
Static excitation systems are used in large and critical generators. These systems work at very high ratings. They are fast and very responsive.
This is how they work:
- They take AC power from the generator terminals.
- They convert AC to DC through thyristors.
- This DC goes to the field winding through slip rings.
The response is very quick because the system uses power electronics. This helps maintain stability when faults occur. Power systems need fast control during faults. Static excitation offers that speed.
These systems are complex. They use advanced engineering. Companies like Siemens and ABB make such systems.
Summary of How Generators Keep Voltage Stable
Generators need excitation to create voltage, and it also helps them control voltage. Instead of changing speed, which affects frequency, they must keep the rotor speed constant. The coil turns are fixed as well, since the generator is already built. This leaves only one option to manage voltage: adjust the magnetic field strength.
So excitation becomes the key method.
When we change excitation, we also change reactive power. Reactive power control keeps voltage stable. Generators are the main source of reactive power in the system.
The load keeps changing. So the voltage keeps changing. So we need an AVR. The AVR keeps voltage near the set point. It does this by adjusting excitation.
The excitation system behind the AVR can be:
- DC excitation,
- AC brushless excitation,
- Static excitation.
Each system controls the field current in its own way. But the goal is the same. They all help the generator keep voltage stable.
Conclusion
Excitation control plays a major role in voltage stability. It manages reactive power. It keeps voltage steady even when the load changes. Without excitation control, the power system cannot run safely.

- Posted In:
- Power System
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 8 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 240K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

