6 Critical Technical Parameters of Ring Main Unit (RMU)
6 Critical Technical Parameters of Ring Main Unit (RMU) https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/maxresdefault-1-1-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gRing Main Unit (RMU) is a factory-assembled, compact medium-voltage switchgear used across power distribution networks. It helps distribute power safely and efficiently. In this article, we’ll explore the 6 critical technical parameters of Ring Main Unit (RMU) that every electrical professional should know.
Before we dive into the parameters, let’s first understand the basic structure and components of an RMU.
Understanding the Structure of a Ring Main Unit (RMU)
A Ring Main Unit includes load break switches (LBS) and circuit breakers (CB) arranged in various configurations.
In a simple setup, you might see:
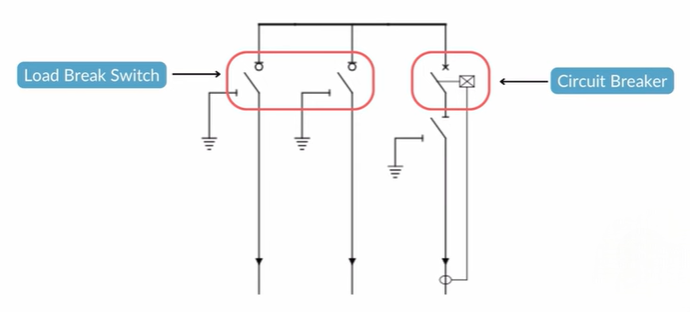
- Two load break switches on the left
- One circuit breaker on the right
This setup is one of the most common configurations. However, RMUs can have many variations. You might find two LBS and one circuit breaker, or one LBS and two circuit breakers, depending on the need.
Each individual switching device is called a function. For example:
- A circuit breaker function
- A load break switch function
The load break switch is different from a circuit breaker or disconnector. It can interrupt normal load currents but not high fault currents.
The technical parameters of a Ring Main Unit (RMU) are primarily based on these switching devices, as they form the heart of the unit.
1. Rated Voltage and Rated Current of Ring Main Unit (RMU)
The rated voltage and rated current are the first and most basic parameters of an RMU.
You can find these ratings on the nameplate of the unit.
Typical rated voltages are 12 kV, 24 kV, or 36 kV.
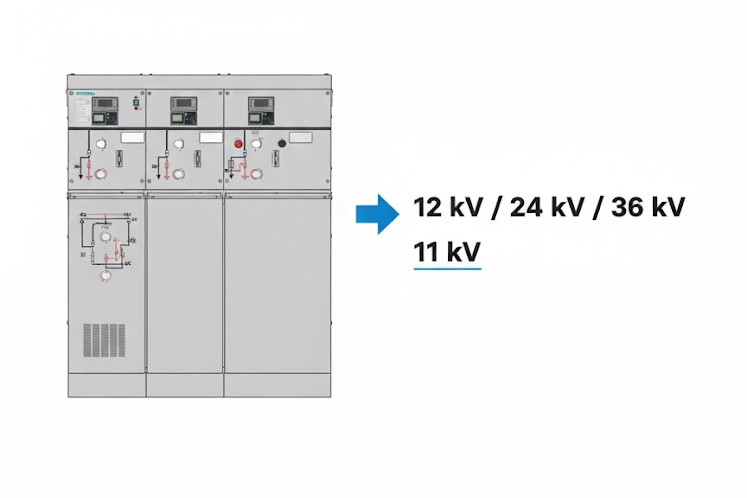
The rated voltage represents the maximum voltage the RMU can carry continuously and safely. For example, the system voltage might be 11 kV, but the rated voltage is 12 kV. The rated value is always a bit higher to ensure safety and reliability.
Similarly, the rated current tells how much current the RMU can carry continuously without overheating. This is often called the continuous current rating.
For RMUs, the rated current is divided between:
- Load Break Switches (LBS): Usually 200A or 630A
- Circuit Breakers (CB): Also 200A or 630A
Most RMUs have rated currents below 1000A.
Sometimes, the LBS and circuit breaker have different current ratings, so both values appear separately on the nameplate.
Along with these, the Basic Insulation Level (BIL) is also mentioned. It includes:
- Rated power frequency voltage
- Rated lightning impulse voltage
These values prove the dielectric strength of the RMU’s insulation.
2. Short-Time Withstand and Breaking Current of Ring Main Unit (RMU)
Next, we come to two important parameters short-time breaking current and short-time withstand current.
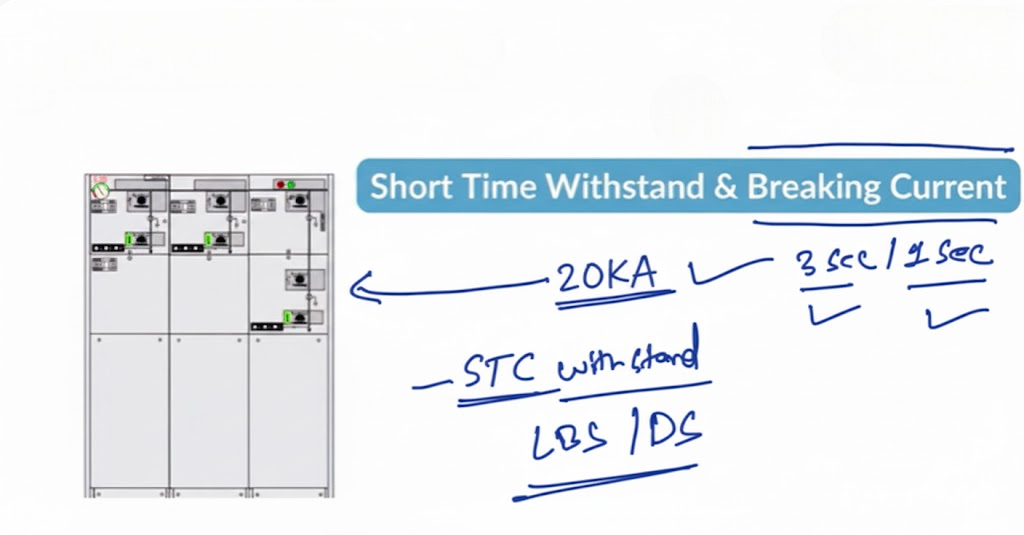
Breaking Current
The breaking current defines the maximum fault current the circuit breaker can interrupt.
During a fault, the current spikes to several kiloamperes (kA). For instance, if a circuit breaker has a rating of 20 kA for 3 seconds, it means:
- It can safely interrupt a fault current of 20 kA.
- It can carry that current for up to 3 seconds before tripping.
This ensures that the circuit breaker can handle high fault conditions without damage.
Short-Time Withstand Current
The short-time withstand current (STC) is slightly different. It applies mainly to non-breaking devices like load break switches or disconnectors.
These devices cannot interrupt fault currents but can withstand them for a short period usually 1 or 3 seconds.
In short:
- Circuit breakers: Can carry and break fault current.
- Load break switches/disconnectors: Can only carry fault current for a short time.
Both ratings appear on the RMU’s nameplate and are vital for ensuring fault protection.
3. Internal Arc Classification (IAC) of Ring Main Unit (RMU)
The internal arc classification (IAC) is one of the most critical parameters for medium-voltage switchgear, including RMUs.
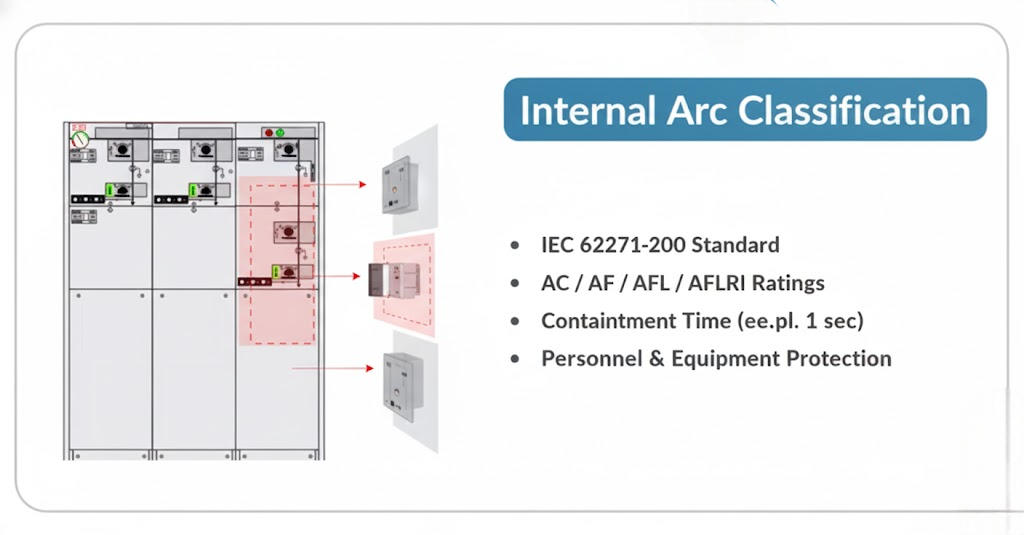
It defines how safely the RMU can handle internal arc faults, one of the most dangerous faults in electrical systems.
You’ll often see IAC ratings written as AFLR 20kA 1s.
Let’s break that down:
- A or B indicates access type.
- A: Accessible only to authorized personnel.
- B: Accessible to the general public (used in public areas).
- A: Accessible only to authorized personnel.
- F, L, R indicate the sides tested.
- F: Front side
- L: Lateral (side)
- R: Rear side
- F: Front side
So, AFLR means the RMU has been tested for arc faults on all sides, front, lateral, and rear.
The 20kA 1s part means the RMU can safely handle a 20 kiloampere arc for 1 second.
These ratings are defined by the IEC 62271-200 standard.
This classification ensures that even during severe faults, the RMU will contain the arc and protect nearby personnel.
4. Number of Functions in Ring Main Unit (RMU)
Each switching device in an RMU is called a function.
For example:
- One circuit breaker = one function
- One load break switch = one function
Based on this, RMUs are categorized as single-function, two-function, three-function, and so on.
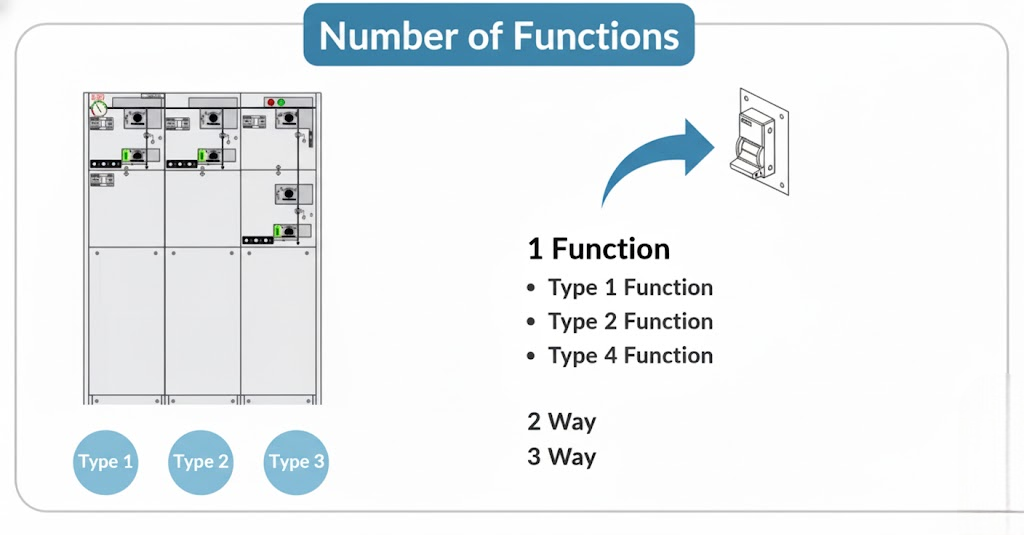
Examples include:
- Single-function RMU: Only one circuit breaker or LBS
- Two-function RMU: One LBS + one circuit breaker
- Three-function RMU: Two LBS + one circuit breaker
The number of functions depends on the application and system design.
For instance:
- Smaller systems might need only a single-function RMU.
- Larger networks may require four- or five-function RMUs.
In some cases, RMUs are also referred to as 2-way, 3-way, or 5-way RMUs.
The selection depends on:
- The type of load being served
- The complexity of the power distribution system
- The need for redundancy or future expansion
5. Extensibility Option of Ring Main Unit (RMU)
The extensibility option adds flexibility to RMUs.
Imagine you have a three-function RMU today. If the load increases in the future, you can extend it by adding new functions instead of installing a new RMU.

This is made possible by extensibility options, which allow easy expansion.
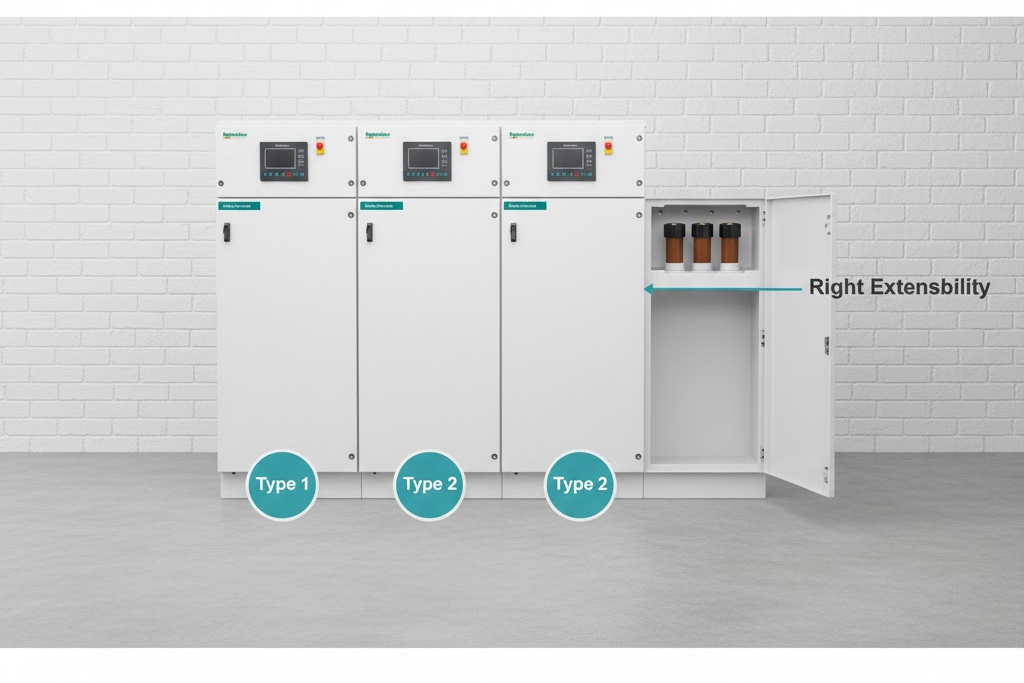
There are three types:
- Right extensibility: Extension possible from the right side

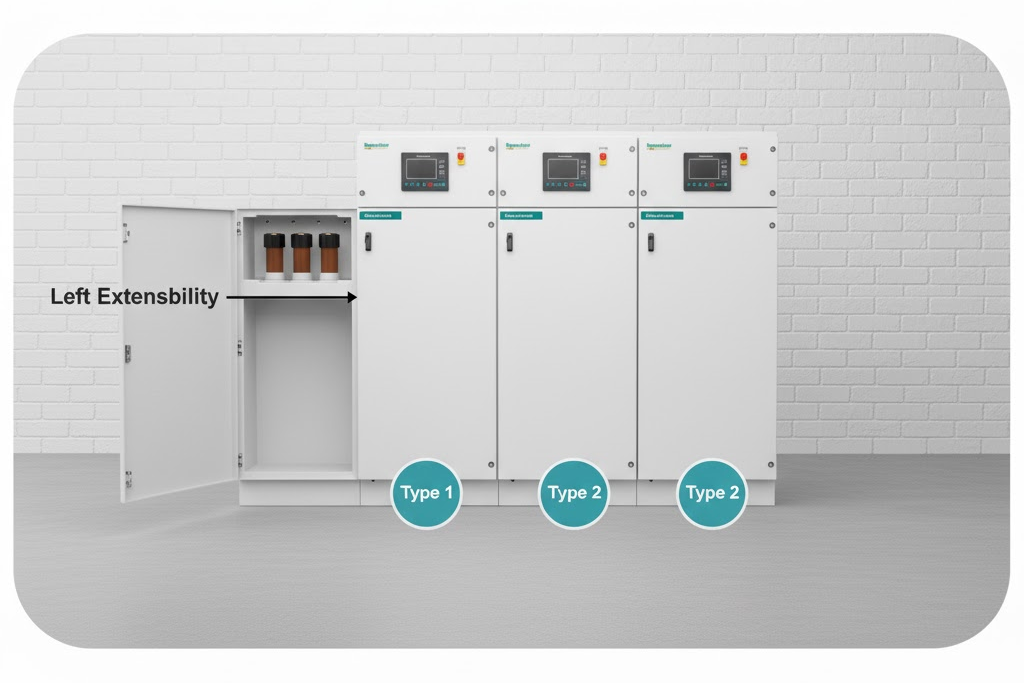
- Left extensibility: Extension possible from the left side

- Dual extensibility: Extensions possible from both sides
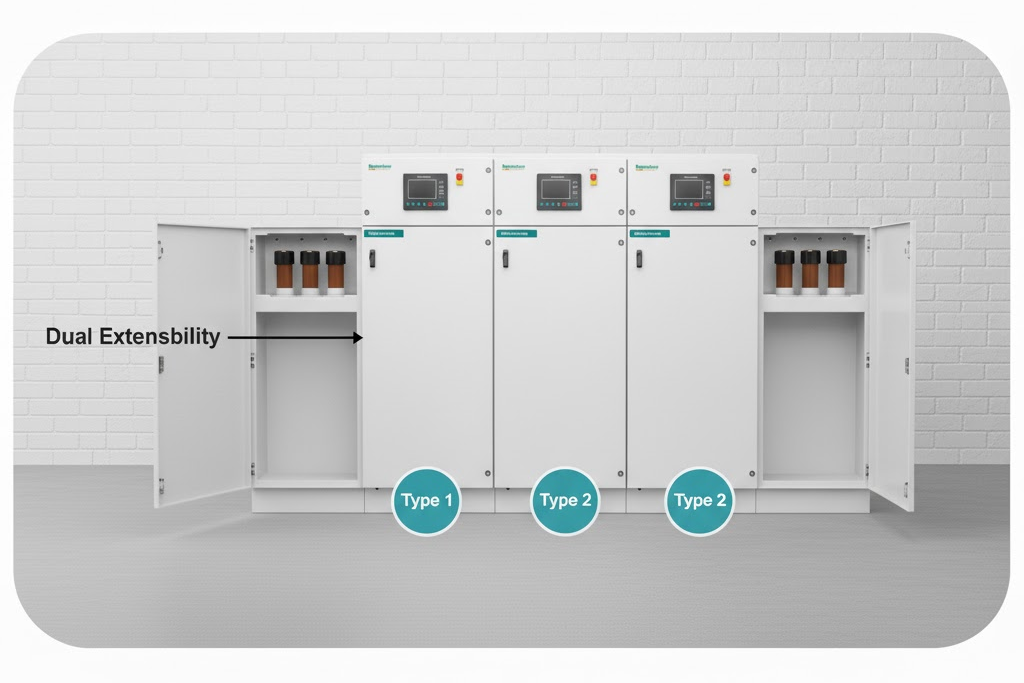

For example, a dual-extensible RMU lets you connect more units from either side.
This option is especially useful when:
- Power demand grows in the future
- You need to add metering or protection functions
- You want to upgrade without major reinstallation
Extensibility makes RMUs a scalable and cost-effective choice for distribution systems.
6. IEC Standard for Ring Main Unit (RMU)
Every RMU must comply with specific IEC standards to ensure performance and safety.
The main standard is IEC 62271-200, which applies to AC metal-enclosed switchgear and control gear for rated voltages from 1 kV up to 52 kV.

This standard defines design, testing, and safety requirements for RMUs.
However, since an RMU includes multiple switching devices, each component also follows its own dedicated IEC standard, such as:
- Load break switches
- Circuit breakers
- Disconnectors
When you check the nameplate of an RMU, you’ll usually find IEC 62271-200 mentioned clearly.
Following these standards ensures that the RMU operates safely, reliably, and in compliance with global electrical norms.
Final Thoughts
The 6 critical technical parameters of Ring Main Unit (RMU) rated voltage and current, short-time withstand and breaking current, internal arc classification, number of functions, extensibility, and IEC standard, are essential for understanding how an RMU works and how it ensures safe power distribution.
Each parameter helps determine how efficiently and safely an RMU can operate under various conditions.
If you want a deeper understanding of these concepts, watch the full video by The Electrical Guy on YouTube. It visually explains each parameter with examples and diagrams for better clarity.

- Posted In:
- Switchgear
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 9 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 250K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

