What is SCADA?
What is SCADA? https://www.theelectricalguy.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/maxresdefault-1024x576.jpg 1024 576 Gaurav Joshi Gaurav Joshi https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/f6a3006f3f7233a71d79d0e705c167ae12516870e5239627478665ae377435b3?s=96&d=mm&r=gA substation operator can open or close a circuit breaker or disconnector without leaving the control room. They can even reset protective relays from the same place. This level of automation is made possible through SCADA in power systems.

Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, is a combination of hardware and software that allows real-time monitoring and control. This article explains what is SCADA, its components, and why it is widely used in power systems.
Table of Contents
- What is SCADA?
- Applications Beyond Power Systems
- Is SCADA a New Technology?
- Why is SCADA Popular in Power Systems?
- Key Functions of SCADA
- Components of SCADA
- Two-Way Communication
- RTUs vs. PLCs
- SCADA in Action
- Advantages of SCADA in Power Systems
- Conclusion
What is SCADA?
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. It is a mix of hardware and software that allows real-time monitoring and control of processes.
In power systems, it helps operators monitor substations 24/7. It connects equipment, sensors, communication protocols, and software under one framework.
Applications Beyond Power Systems
It operates in many fields beyond power systems. Industries widely use it in:
- Water management – for precise chemical dosing.
- Oil and gas industries – for monitoring leaks across pipelines.
- Transportation – in railway signaling and airport systems.
- Manufacturing – for industrial automation and process control.
Though used in many fields, we will focus here on SCADA in power systems.
Is SCADA a New Technology?
SCADA is not new. It has been in use since the 1960s and 1970s. It evolved with the growth of computers and networks.
Computers and networks were limited earlier. Advances in LAN, wireless systems, and communication improved. It is not new; it has become more advanced with technology.
Why is SCADA Popular in Power Systems?
The popularity of SCADA in power systems comes from its flexibility and features. Let’s see why.
Problem Without Automation
Imagine a distribution substation without automation. If a fault occurs:
- Operators will not know about it unless a customer reports it.
- Engineers may only detect it while patrolling.
- Locating the fault will take time.
- Calling teams and fixing the issue will take more time.

In the best case, it may take 40 minutes. In the worst case, it could take hours. This delay shows the need for automation.
Solution With SCADA
Now imagine the same substation with SCADA. If a fault occurs:
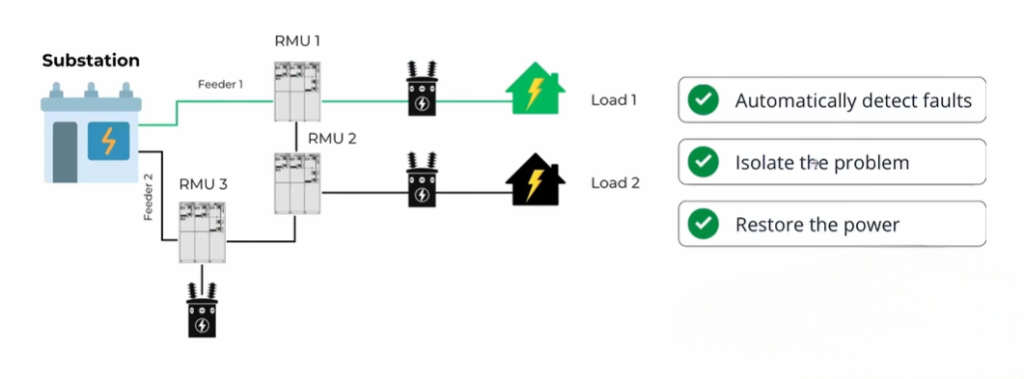
- The grid detects the fault automatically.
- The system isolates the faulty section.
- Power is restored quickly.
All this happens within minutes, without human intervention. It is widely used as it delivers speed and efficiency.
Key Functions of SCADA
The name SCADA explains its two main functions:
- Supervisory Control – Operators can take actions based on the data available.
- Data Acquisition – It collects data. Operators make informed decisions using it.
Without data, decisions would be guesswork. It ensures that operators see real-time data and act on it.
Components of SCADA
To understand what is SCADA, we must look at its components.
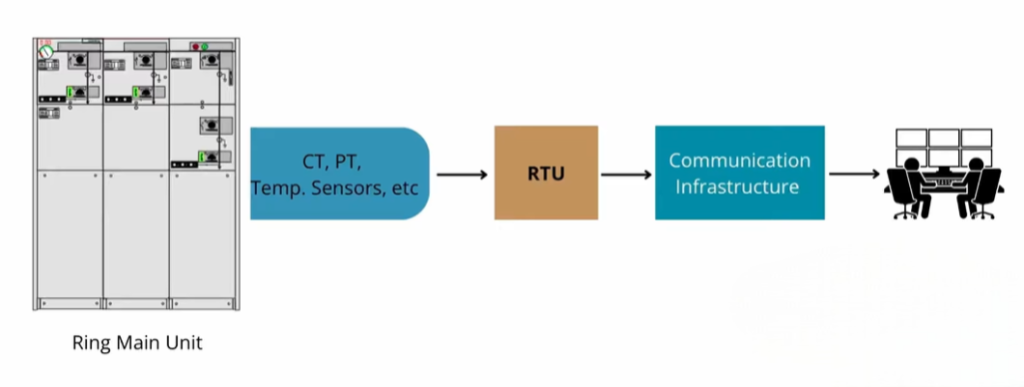
Sensors
SCADA starts with sensors that measure key parameters. In substations, common sensors include:
- Current transformers (CTs)
- Potential transformers (PTs)
- Temperature sensors
- Humidity sensors, etc
These sensors collect values for current, voltage, temperature, and more.
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
The data from sensors is scattered across equipment. RTUs collect this data.
Each ring main unit (RMU) can have a dedicated RTU. The RTU gathers sensor data and consolidates it. This data is also sent to a master terminal unit.
Communication Infrastructure
The system transmits the collected data through communication lines. These lines may be wired or wireless.
Protocols like Modbus and IEC 61850 are widely used. They ensure smooth communication in substation automation.
Software
Finally, operators need software to view and interpret the data. The software displays equipment status, current, voltage, and faults on screens in the control room.
This complete setup of sensors, RTUs, communication, and software forms the SCADA system.
Two-Way Communication
One key advantage of SCADA is two-way communication.
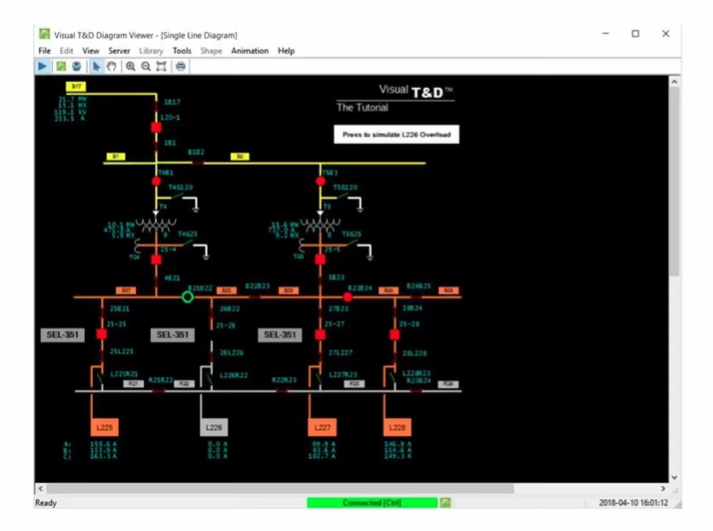
- Operators can send commands from the control room to equipment.
- Commands go through RTUs to devices like ring main units.
- Operators can open or close breakers, change transformer taps, start or stop generators, and reset relays.
This reduces the need for operators to enter risky areas like switchyards. It makes the work safer and faster.
RTUs vs. PLCs
In substations, RTUs are common. They are designed for remote operations.
Industrial processes use Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). For example, operators control water pumps with them. In power systems, operators prefer RTUs.
SCADA in Action
A single-line diagram of a substation on SCADA shows every switch and breaker. Operators can:
- Track switch positions.
- Operators identify whether a fault is on a busbar or a feeder.
- Decide which switches to open or close.
- Restore power without delays.
Clear visibility improves safety and efficiency.
Advantages of SCADA in Power Systems
- Fast fault detection – It identifies faults within minutes.
- Automatic isolation – It separates faulty sections quickly.
- Power restoration – done automatically without human delay.
- Remote control – operators work from control rooms.
- Improved safety – less risk to operators in switchyards.
Conclusion
Now you know what is SCADA, its functions, and why it is vital in power systems. It enables operators to monitor, control, and restore power efficiently. It has become the backbone of substation automation. For a clearer understanding, watch the full video on SCADA by TheElectricalGuy.

- Posted In:
- Power System
Gaurav Joshi
Gaurav, also known as TheElectricalGuy, is an accomplished electrical engineer with over 8 years of experience in the high and medium voltage switchgear industry. In addition to his professional endeavors, Gaurav has made significant contributions to the global electrical engineering community through his highly successful YouTube Channel. With over 240K subscribers and a prestigious silver play button from YouTube, he has become a trusted resource for electrical engineers worldwide. Gaurav's dedication to sharing knowledge extends to the creation of comprehensive courses, which have already attracted over 5000 students eager to enhance their skills in the field.
All stories by: Gaurav Joshi

